“Alumni are the reflection of our past, representation of our present and link to our future,” says Chancellor
17 cohorts, 16 convocations and 1800 alumni all over the world in various top positions
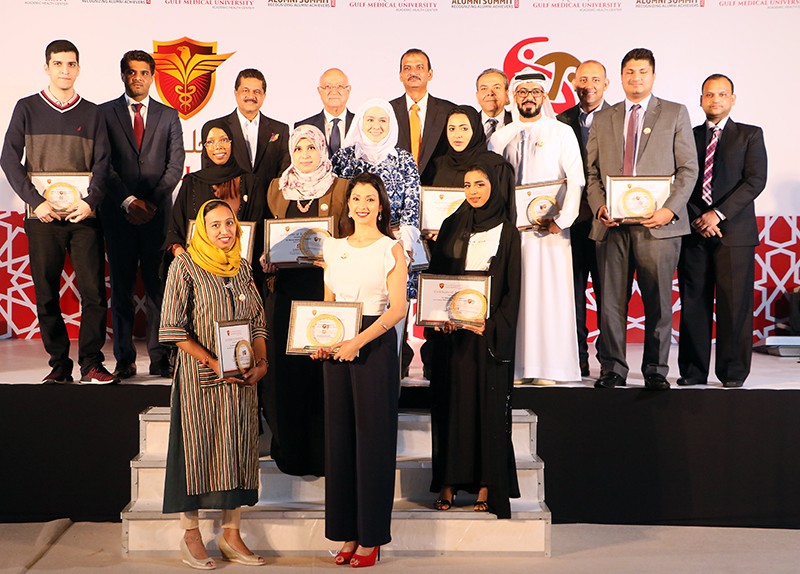
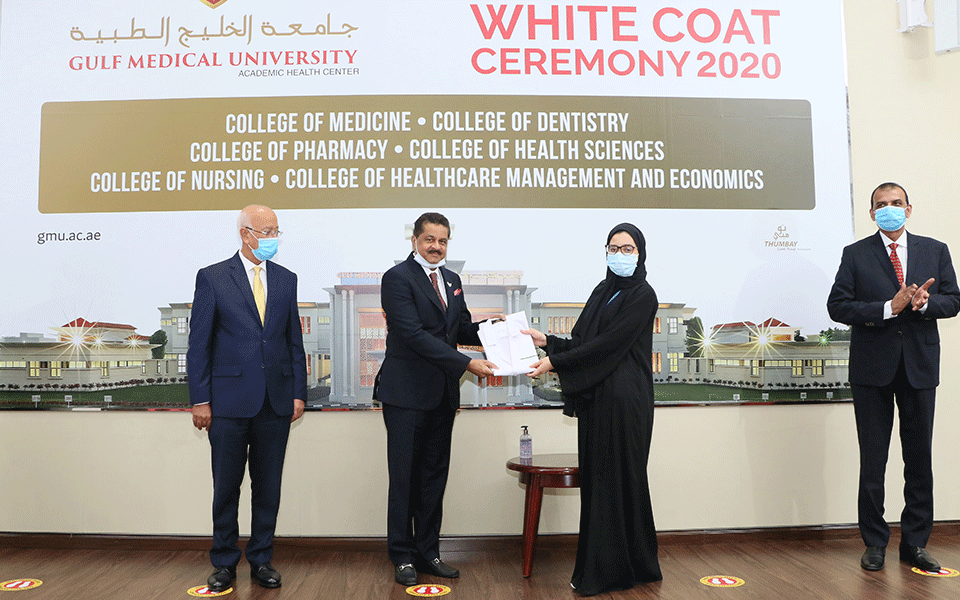
Ajman: Gulf Medical University (GMU), Ajman recognized the most outstanding accomplishments of its alumni at the ‘GMU Global Alumni Summit 2020’ organized by the GMU Students Affairs Department, held at Thumbay Medicity on 29th February 2020.
The event brought together GMU alumni from around the world, joined by the academic leadership of GMU, faculty, staff and students, in a celebration of the significant contributions of the alumni community to their communities and professions. The event recognized their most outstanding achievements. The awards in honor of the GMU Achievers were presented by Dr. Thumbay Moideen, Founder, President Board of Trustees, GMU who also officially released the Alumni E-newsletter and the Alumni Portal.
In his welcome address, Prof. Manda Venkatramana, Vice Chancellor – Academics mentioned that GMU’s alumni now has 1803 graduates, with 70% females and 30% male graduates, spread across the world, with UAE nationals constituting 10% of the alumni, GCC nationals 7%, other Arabs 14%, Asians 44%, Africans 16% and other nationals 10%.
Addressing the alumni, Prof. Hossam Hamdy, the Chancellor of GMU outlined the significant achievements of the University in recent times. The Chancellor also announced several benefits for the alumni, including scholarships for post-graduate programs, adjunct faculty positions at GMU, employment opportunities and full access to GMU’s e-library learning resources. “You are our best ambassadors offering invaluable advocacies across your personal and professional networks. You are the reflection of GMU’s past, representation of its present and the link to its future,” he said to the alumni.
Awards were presented to the following alumni achievers:
Healthcare: Government Service UAE - Dr. Noha Yaseen, Consultant Cardiologist, Al Qasimi Hospital, Sharjah; Dr. Asma Abdillahi Ali, CCAD, Semi-Government by Mubdhala, Abu Dhabi government; Ms. Ayesha Mohammed Abdulla Kajoor Al Nuaimi.
Healthcare: Research - Dr. Ahmad Ashraf Fakhri Ghazal.
Healthcare Delivery System: Entrepreneurship – Dr. Ismail Sayeed, Founder & CEO, ViOS; Ms. Jameela Arif Hussain; Dr. Sheetal Bambhani.
Healthcare Delivery System: Private Sector / Leadership - Dr. Shihad Khader, Chief Operating Officer, Thumbay Hospital Fujairah; Dr. Meera Obaid AlSalami.
Healthcare Delivery System: NGO / Humanitarian Service - Dr. Faraj Khalid Faraj Mohamed Almehairbi.
Arts: Dr. Marwa Abdulwahid Alalwani, Dentist, Munich Dental Clinic.
The awardees recounted their experiences as GMU students, and explained how those experiences continue to enrich their professional lives even today. They thanked Dr. Thumbay Moideen for creating such a wonderful university which shaped their lives and career achievements. Current GMU students entertained their alumni with various talent performances.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Kochi (PTI): The ruling CPI(M) in Kerala on Wednesday inaugurated one of the completed stretches of NH-66, hours ahead of its dedication to the nation by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in protest against the exclusion of state PWD minister P A Mohammed Riyas from the PM's event.
Riyas, reportedly, will hold a roadshow on one of the completed stretches of the National Highway-66 that is scheduled to be inaugurated by the PM.
The Thalappady-Chengala stretch of NH 66 was inaugurated by CPI(M) MLA C H Kunhambu.
The roadshow by Riyas will be held on the Vengalam-Ramanattukara stretch of the Kozhikode bypass.
Both these stretches, which were upgraded to six lanes and already opened to the public, were set to be inaugurated by the PM at 12.30 pm here.
ALSO READ: Assam govt drops ex-president Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed's name from medical college in Barpeta
According to government sources, Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan won't attend the event, though his name is included in the programme schedule. However, no particular reason was cited for his decision to skip the event.
State Ministers M B Rajesh and K Krishnankutty, who have been invited to the PM's event, also said they are not taking part because of personal reasons.
In response to the CM and other ministers' decision, state BJP president Rajeev Chandrasekhar told reporters that, as per protocol Vijayan, being the head of the state, was invited for Modi's official event, and if the Marxist veteran was aggrieved over his son-in-law (Minister Riyas) not being there, that is his problem.
"As head of the state, the CM was invited in accordance with the protocol. It is nowhere said that the CM's son-in-law (Riyas) and other family members also have to be invited. If they have a problem with it, so be it. That is what I have to say," the BJP leader said.
"It was for the CM to decide who should accompany him. Elections will be held in the state in around 30 days. The CPI(M) is trying to create a controversy now as they know that after 30 days, Vijayan will not be CM and Riyas will not be a minister," Chandrasekhar said.
He further said that the CM was aware of the PM's visit 5-6 days in advance, and he did not say anything about who all should be invited.
"Why did he not say anything? This is all an attempt to create controversy. If you (CM) wanted a certain minister to accompany you, it should have been communicated to the government of India in advance. Why did you not do that? From what I know, the CM did not say anything to the Centre," the BJP state president claimed.