The Saudi space mission is slated to launch on May 21, 2023. Rayyanah Barnawi, the first Arab Muslim female astronaut, and Ali AlQarni will travel to the International Space Station on this day.
The mission was started on September 22 of last year as a part of the Kingdom's astronaut programme. The mission is a representation of Saudi Arabia's aspirations for space exploration and one of Vision 2030's objectives.
The Saudi space mission will take off from American soil, but more significantly, it represents a historic turning point for the Kingdom. 14, ground-breaking scientific experiments will be carried out by the astronauts in microgravity to advance our understanding of how to best support future space exploration by people.
The outcomes will strengthen the Kingdom's position in space exploration on a global scale and advance efforts to better serve humanity. It will benefit Saudi research institutions and advance science for further space exploration.
Additionally, the astronauts will stream live three educational awareness experiments to 12,000 Saudi students .
Once this trip is complete, the Kingdom will be one of the select few nations to have sent two astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) at the same time. If it is successful, the Kingdom's standing in space exploration and humanitarian aid will improve on a worldwide scale.
A significant turning point will be reached for the Saudi astronaut programme. The programme aims to fulfil the objectives of Vision 2030 by preparing future astronauts and engineers for space through high-quality educational and training programmes, involvement in scientific experiments, a global research, and future space-related missions.
Here are some additional details about the Saudi space mission:
- The mission will be launched from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
- The astronauts will travel to the ISS on a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft.
- The astronauts will spend eight days on the ISS, during which time they will conduct a variety of scientific experiments.
Explained : International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large spacecraft in orbit around Earth. It serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is the ninth space station to be inhabited by crews, following the Soviet and later Russian Salyut, Almaz, and Mir stations and the American Skylab. It is the largest artificial object in the Solar System and the largest satellite in low Earth orbit, regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth's surface. It maintains an orbit with an average altitude of 400 kilometres (250 mi) by means of reboost manoeuvres using the engines of the Zvezda Service Module or visiting spacecraft. The ISS circles the Earth in roughly 93 minutes, completing 15.5 orbits per day.
The ISS was a joint project of five space agencies: the United States' NASA, Russia's Roscosmos, Japan's JAXA, Europe's ESA, and Canada's CSA. The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. Construction of the ISS began in 1998 and was completed in 2011. The first crew arrived in 2000 and the station has been continuously occupied since then.
The ISS has been visited by astronauts and cosmonauts from all over the world. It has also been the site of many scientific experiments, including studies of the effects of microgravity on the human body, the development of new technologies, and the exploration of space.
The ISS is a symbol of international cooperation and a testament to the human ability to achieve great things. It is a valuable asset to the world and will continue to be used for scientific research and exploration for many years to come.
Additional information on the ISS is provided below.
- It is about the size of a football field.
- It weighs about 460 tons.
- It orbits Earth at an average speed of 17,500 mph.
- It has been continuously occupied since November 2, 2000.
- More than 200 people from 19 countries have visited the ISS.
- The ISS has cost about $150 billion to build and operate.
- The ISS is expected to be operational until at least 2024.
Girish Linganna
Aerospace & Defence Analyst
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
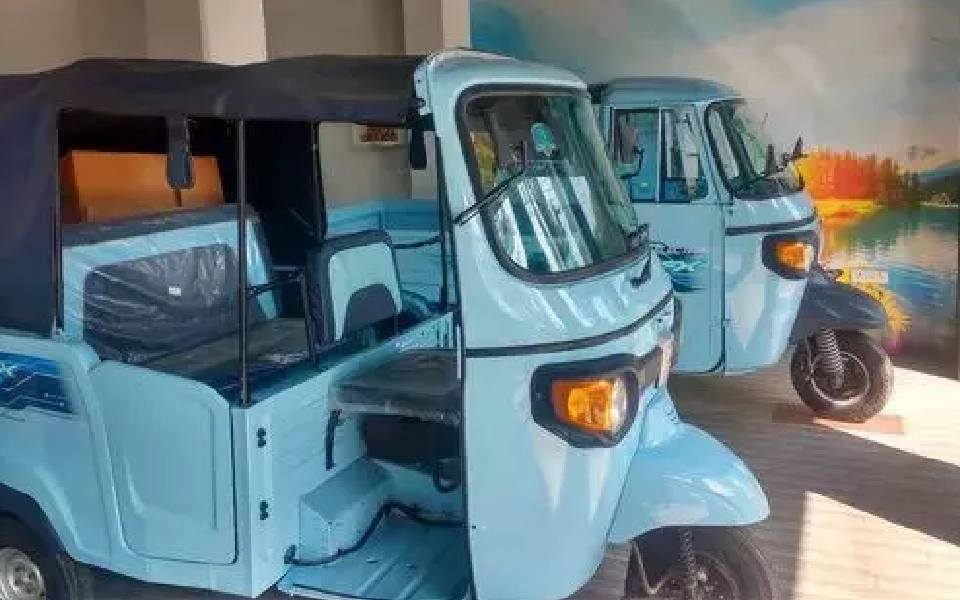
Mangaluru: DC Mullai Muhilan issued orders permitting electric auto rikshaws and autos running on ethanol and methanol to ply across the district freely. Despite being issued on July 26, the orders were released to the public on Tuesday.
The orders retract the earlier notifications issued on November 24, 2022 and January 1, 2023.
In zone-1, E-auto rikshaws and rikshaws running on methanol and ethanol were ordered to be painted yellow on the front side till the middle and black on the rear till the middle. They were also directed to bear square shaped stickers of blue colour with identification numbers issue by the police department.
ALSO READ; Two youngsters seriously injured in Udupi after scooter collides with parked bus
Similar rikshaws in zone-2 were also directed to be painted in the same way. However the orders about having police issued yellow coloured circular identification stickers has been cancelled. DC has directed the RTO officers to take strict measures for the implementation of these rules.
Mangalore city SP and DSP have been permitted to put up necessary notice boards regarding these rules.
DC has also authorized the commissioner of Municipality and the officials of the local bodies to fix parking zones and vehicle stops in their areas.





