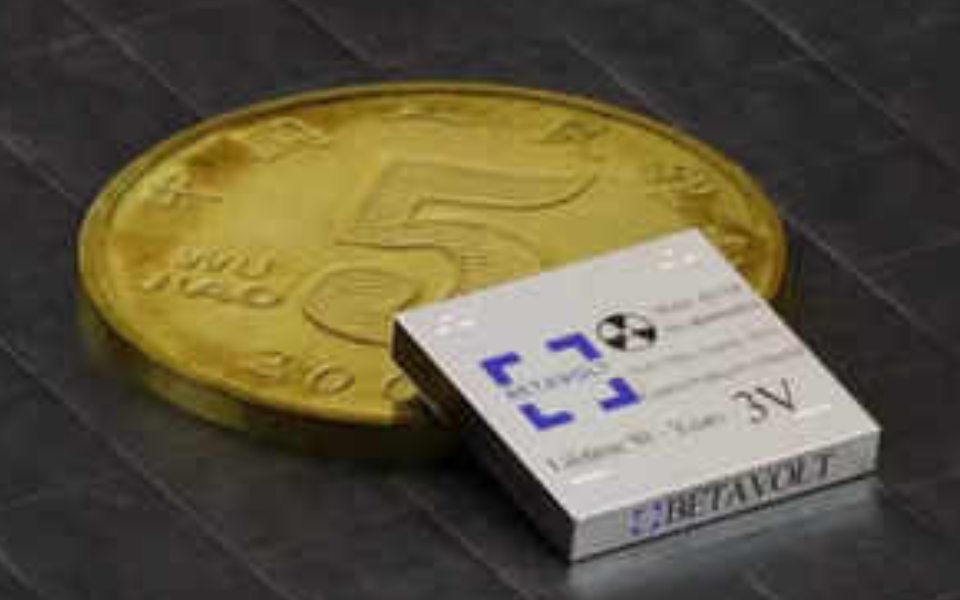
Betavolt, a Chinese startup, claims a groundbreaking achievement with the development of a nuclear battery that can power smartphones for an impressive 50 years without requiring charging. This nuclear battery, deemed the world's first miniaturized atomic energy system, utilizes 63 nuclear isotopes packed into a module smaller than a coin.
The technology involves converting energy released by decaying isotopes into electricity, a concept first explored in the 20th century and now realized by Betavolt. The startup has initiated pilot testing and plans to mass-produce the battery for various applications, including smartphones and drones.
In their press release, Betavolt stated, "Betavolt atomic energy batteries can meet the needs of long-lasting power supply in multiple scenarios, such as aerospace, AI equipment, medical equipment, microprocessors, advanced sensors, small drones, and micro-robots." They believe this innovation will provide China with a competitive advantage in the AI technology era.
The initial nuclear battery by Betavolt delivers 100 microwatts of power with a voltage of 3V, measuring a tiny 15x15x5 cubic millimeters. The company aims to produce a battery with 1 watt of power by 2025. The small size allows for multiple units to be connected, increasing power output, envisioning a future where mobile phones never need charging, and drones can fly indefinitely.
Ensuring safety, Betavolt's design features a layered structure to prevent fire or explosions when subjected to sudden force. The battery can operate in a wide temperature range, from -60 degrees Celsius to 120 degrees Celsius.
To create the battery, Betavolt used nickel-63, a radioactive element, as the energy source, employing diamond semiconductors for energy conversion. The team developed a thin single-crystal diamond semiconductor and placed a nickel-63 sheet between two diamond semiconductor converters. The radioactive source's decay energy is then converted into electrical current.
Addressing radiation concerns, Betavolt assures users of safety, stating no external radiation. It is deemed suitable for use in medical devices inside the human body, such as pacemakers and cochlear implants. After the decay period, the isotopes transform into a stable, non-radioactive isotope of copper, posing no environmental threat.
The BV100 battery by Betavolt is also considered more secure than conventional batteries, not catching fire or exploding when punctured or exposed to high temperatures.
The development of miniaturized nuclear batteries has been a longstanding goal, and Betavolt's breakthrough technology has the potential to revolutionize electronics by eliminating the need for chargers or portable power banks.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Bengaluru (PTI): The Karnataka High Court on Monday extended the interim relief given to Bollywood actor Ranveer Singh till March 9, in a case related to mimicking a character from the movie, 'Kantara Chapter-1', and allegedly mocking a deity.
The actor had approached the High Court seeking the quashing of the FIR against him for mimicking Rishab Shetty's role as 'Chavunda' deity in the movie.
While mimicking, Singh had called the deity a "ghost". The actor was asked to appear before the court in person on Monday.
Appearing on behalf of the actor, his counsel Sajjan Poovayya said Singh was stuck in London and was unable to reach Bengaluru due to the conflict in West Asia.
The complainant, who is a lawyer, alleged that his religious sentiments were hurt by calling the deity a ghost. On the directions of a local Court, the police registered a case against the actor.
The High Court on February 24 granted interim relief to the actor with directions to the police not to take any coercive steps against him.