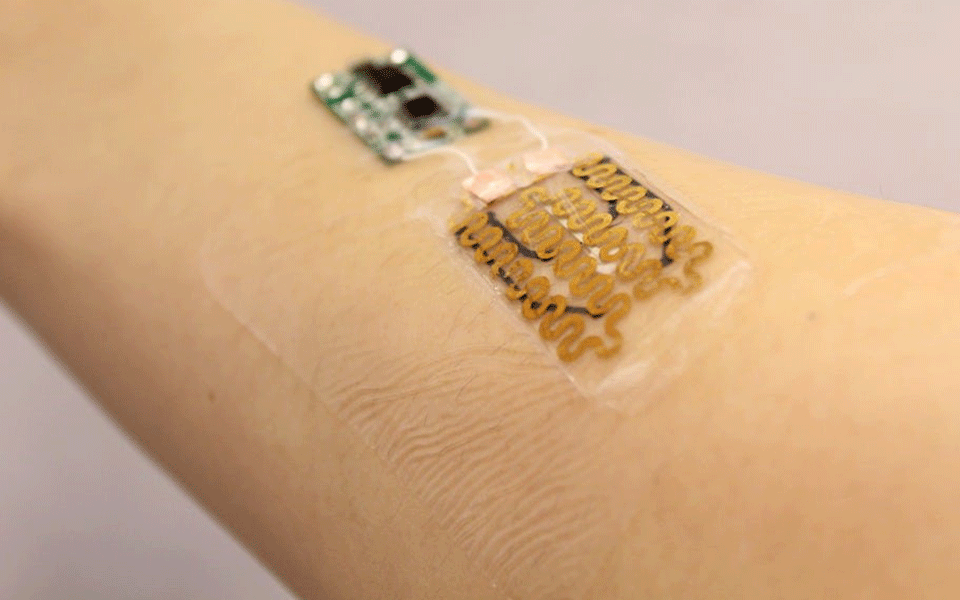
New York, July 7: Researchers have developed a prototype bandage designed to actively monitor the condition of chronic wounds and deliver appropriate drug treatments to improve the chances of healing.
While the lab-tested bandages remain to be assessed in a clinical context, a study, published in the journal Small, said the aim is to transform bandaging from a traditionally passive treatment into a more active paradigm to address a persistent and difficult medical challenge.
According to the researchers, chronic skin wounds from burns, diabetes and other medical conditions can overwhelm the regenerative capabilities of the skin and often lead to persistent infections and amputations.
"We have been able to take a new approach to bandages because of the emergence of flexible electronics," said co-author Sameer Sonkusale, Professor at Tufts University in the US.
The researchers designed the bandages with heating elements and thermoresponsive drug carriers that can deliver tailored treatments in response to embedded pH and temperature sensors that track infection and inflammation.
They said that pH of a chronic wound is one of the key parameters for monitoring its progress. Normal healing wounds fall within the range of pH 5.5 to 6.5, whereas non-healing infected wounds can have pH well above 6.5.
Temperature is also an important parameter, providing information on the level of inflammation in and around the wound, they added.
While the smart bandages in this study combine pH and temperature sensors, the team have also developed flexible sensors for oxygenation -- another marker of healing -- which can be integrated into the bandage.
Inflammation could also be tracked not just by heat, but by specific biomarkers as well, the researchers said.
A microprocessor reads the data from the sensors and can release drug on demand from its carriers by heating the gel.
The entire construct is attached to a transparent medical tape to form a flexible bandage less than 3 mm thick. Components were selected to keep the bandage cheap and disposable, except for the microprocessor, which can be re-used.
The researchers noted that smart bandages could provide real time monitoring and delivery of treatment with limited intervention from the patient or caregivers.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
New Delhi (PTI): Opposition MPs have submitted notices in both Houses of Parliament seeking a motion for the removal of Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) Gyanesh Kumar, sources said on Friday.
As many as 130 Lok Sabha MPs and 63 Rajya Sabha MPs have signed the notice, a source said.
The signatories include members from all the INDIA bloc parties, the source said, including the Aam Aadmi Party, which has also backed the move despite no longer being formally part of the opposition alliance, the source said.
Some independent MPs have also signed the notice, and several others have expressed interest in joining the initiative, the source added.
This is the first time a notice has been moved seeking the removal of the CEC. According to sources, the notice lists seven charges against Kumar, including alleged "partisan and discriminatory conduct in office", "deliberate obstruction of investigation of electoral fraud" and "mass disenfranchisement."
The opposition parties have accused the CEC of aiding the ruling BJP on several occasions, especially with the ongoing Special Intensive Revision (SIR) of electoral rolls, which they alleged aims to help the saffron party at the Centre.