An elderly man with difficulty in walking, a young woman with inability to speak, a child with vision loss. These are few of the different scenarios we come across in people with stroke. It is heart wrenching to see young and old people alike having to face these disabilities. This world stroke day, let us increase our understanding of stroke.
As rightly said by the Dutch philosopher Desiderius Erasmus ‘Prevention is better than cure', Stroke is an event which can be prevented by simple measures but may leave one disabled for life if neglected. In India, around 1.8 million people suffer from a stroke every year and many survivors face disability. Having one stroke increases the risk of another or recurrent stroke. Since 80% of the strokes are preventable, it becomes all the more important for us to have a thorough knowledge about this disease and its prevention.
What is stroke?
Stroke happens when blood flow to a part of your brain is impaired. Due to the lack of oxygen rich blood, that part of the brain tissue undergoes cell death, leading to brain damage, disability and death.
Stroke can happen in one of the two ways:
1. Ischaemic stroke- It occurs when blood supply to the brain is blocked, which can be due to an embolism stroke or a thrombotic stroke.
Embolic stroke: In embolic stroke, blood clots forms somewhere in the body (usually the heart) and travels through the bloodstream, into the brain, blocking the blood vessel, causing stroke.
Thrmobotic stroke: In this type of ischaemic stroke, the blood flow is impaired due to a blockage in one or more of the arteries that supply blood to the brain. This process is known as thrombosis.
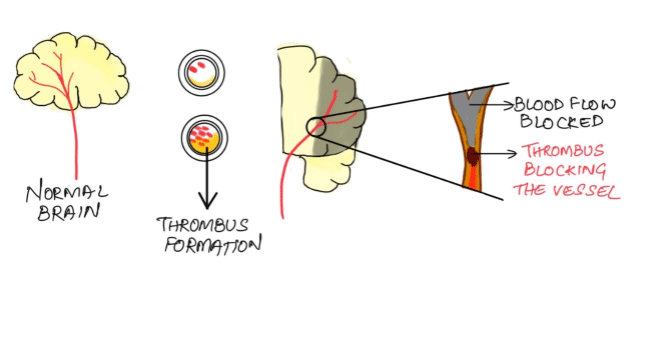
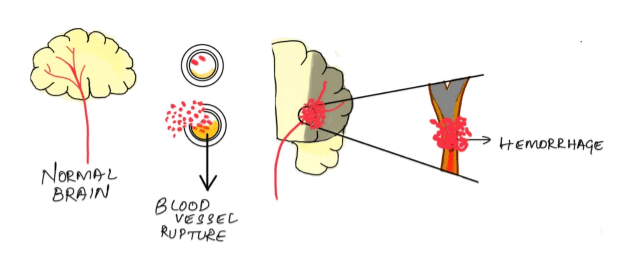
2. Hemorrhagic stroke- This occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. Hemorrhage can be caused by a number of disorders that affect the blood vessels, including high blood pressure and cerebral aneurysms.
What are the risk factors?
High blood pressure
►High cholesterol
►Atherosclerosis
►Smoking
►Physical inactivity
►Diabetes
►Atrial fibrillation
►Obesity
Traditionally, increased age has been found to be a risk factors for stroke. However, due to the change in life style in the current generation, increasing incidence of stroke in young have been reported. Risk factors may not be identified and treated in middle aged adults and hence it is important to screen for high BP and high cholesterol in middle aged adults.
What are the symptoms and signs of stroke?
An easy way to remember the most common sign of stroke and how to respond is with the acronym FAST
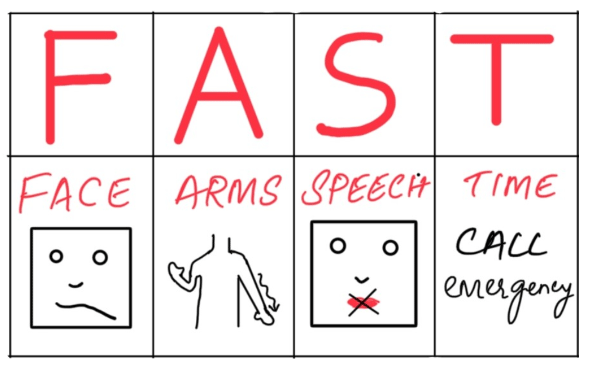
F- Face drooping: ask the person to smile
Does one side droop?
A- Arm weakness: ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S- Speech difficulty: ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Are the words slurred?
T- Time to call emergency service: IF the person shows any of these signs, call emergency service immediately.
Other signs and symptoms include:
Sudden giddiness, loss of balance, difficulty in walking
Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
Sudden severe headache with no known cause
Sudden numbness or weakness of face, arm or leg – especially on one side of the body
Sudden confusion or difficulty in understanding others.
How is stroke diagnosed?
Stroke is diagnosed initially based on the patients’ symptoms and clinical examination. Initial evaluation is done to assess the level of consciousness and function, to determine the cause, location and severity of stroke. Further confirmation is obtained by imaging studies, namely Computerised Tomography (CT scan) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI brain). Other tests that may be required include ECG, 2D ECHO and Neck vessel Doppler.
Treatment:
In stroke, “Time is brain.” A stroke can cause permanent damage within minutes to hours. Its treatment and outcome depends on how fast you get to the hospital. Early treatment can minimize the extent of brain damage, thus reducing the morbidity associated with this condition. Treatment also depends on the type of stroke, whether ischemic or hemorrhagic.
Treatment following a stroke generally falls into three therapeutic approaches:
►Emergency medical or surgical care given immediately after a stroke to minimize the extent of injury
►Treatment to prevent a second or recurrent stroke
►Rehabilitation to improve disabilities that result from stroke
Ischemic stroke treatment:
Medications:
Medication or drug therapy is the most common treatment for ischemic stroke. These include:
1. Thrombolytics: These are drugs that break up and dissolve existing clots. The thrombolytic drug-Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-PA) can be effective if a person receives it intravenously (through a vein) within 4.5 hours from the onset of stroke symptoms. This highlights the importance of seeking early medical assistance for any individual with symptoms of stroke, so that timely intervention can be provided.
2. Antithrombotics: Antithrombotics prevent the formation of blood clots in a brain artery. There are two kinds of blood-thinning medications—antiplatelets and anticoagulants
► Antiplatelet drugs prevent clotting by decreasing the activity of platelets, which are blood cells that cause blood to clot. By reducing the risk of blood clots, these drugs lower the risk of ischemic stroke. The most widely known and used antiplatelet drug is aspirin. Other antiplatelet drugs include clopidogrel, ticlopidine, and dipyridamole.
► Anticoagulants lower the risk of stroke by reducing the clotting property of the blood. The most commonly used anticoagulants include warfarin, heparin, enoxaparin, and dalteparin. The newer anticoagulants include dabigatran, apixaban, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban.
Endovascular procedures- Mechanical Thrombectomy:
► These have been the new revolutionary treatment options in the management of stroke. Clot removal involves threading a catheter through the artery to the site of the blockage and removal of clot through suction, or other devices.
Surgical procedures:
►The carotid arteries, located in the neck, are the main suppliers of blood to the brain.
►Carotid endarterectomy involves surgical removal of obstructing plaque from the inside of a carotid artery which widens the artery.
Hemorrhagic stroke:
Treatment for hemorrhagic stroke involves finding the source of the blood leak and controlling it. It requires supportive care in the form of controlling the blood pressure and other symptomatic treatment. In severe cases, surgery may be required to relieve the intracranial pressure caused by the bleeding.
Rehabilitation:
► Rehabilitation is vital to stroke recovery.
► Physical, occupational and speech therapy is the main form of rehabilitation for most people with stroke. These therapies use training and exercises to restore movement, balance, speech and skilled activities.
► Psychological or psychiatric help can assist many people suffering from depression, anxiety and frustration, which are common disabilities in people with stroke. Therapy, along with medication, can help ease some of the mental and emotional problems that result from stroke.
Prevention of stroke
There are several steps you can take to reduce stroke risk:
► Eat healthy: Choose healthy foods including foods with less salt, with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
► Physical Activity: Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy weight and keeps your heart and blood vessels healthier. Adults aged 18 years or older should get at least 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) of physical activity each week.
► Avoid smoking
► Avoid alcohol
► Screen for lifestyle disorders such as high BP, high cholesterol, diabetes and obesity. Follow up regularly if diagnosed with any of these diseases.

Dr. Salma Suhana
Assistant professor, Department of Neurology
Yenepoya Medical College and Hospital
Deralakatte, Mangalore.
Consultant Neurologist
Medi Nerv, Mangalore.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
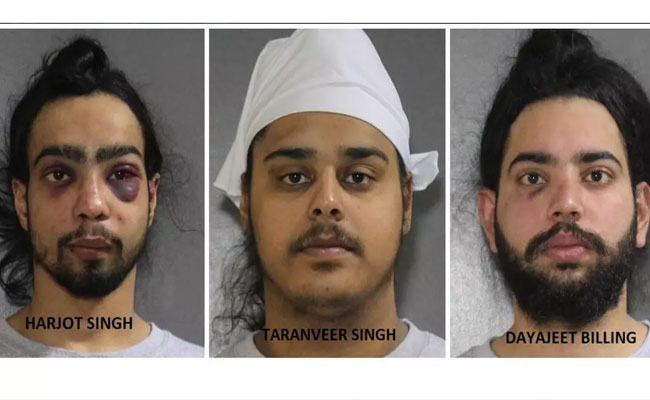
Ottawa (PTI): Three Indian nationals have been arrested by Canadian police on an anti-extortion patrol and charged after bullets were fired at a home.
Harjot Singh (21), Taranveer Singh (19) and Dayajeet Singh Billing (21) face one count each of discharging a firearm, and all have been remanded in custody until Thursday, the Surrey Police Service (SPS) said in a statement on Monday.
The suspects were arrested by patrol officers after an early morning report of shots fired and a small fire outside a home in Surrey's Crescent Beach neighbourhood, the LakelandToday reported.
On February 1, 2026, the SPS members were patrolling in Surrey’s Crescent Beach neighbourhood when reports came in of shots being fired and a small fire outside a residence near Crescent Road and 132 Street.
The three accused were arrested by SPS officers a short time later, the statement said.
SPS’s Major Crime Section took over the investigation, and the three men have now been charged with Criminal Code offences, it said.
All three have been charged with one count each of discharging a firearm into a place contrary to section 244.2(1)(a) of the Criminal Code.
The investigation is ongoing, and additional charges may be forthcoming. All three have been remanded in custody until February 5, 2026.
The SPS has confirmed they are all foreign nationals and has engaged the Canada Border Services Agency, it said.
One of the suspects suffered injuries, including two black eyes, the media report said.
Surrey police Staff Sgt. Lindsey Houghton said on Monday that the suspect had refused to comply with instructions to get out of the ride-share vehicle and started to "actively resist."
"As we were trained, he was taken to the ground and safely handcuffed," said Houghton.
A second suspect with a black eye was also injured in the arrest after refusing to comply, Houghton said.
The arresting officers were part of Project Assurance, an initiative that patrols neighbourhoods that have been targeted by extortion violence.
Houghton said the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) is also involved because the men are foreign nationals, and the trio may face additional charges.
It's not clear if the men are in the country on tourist visas, a study permit, or a work permit, but Houghton said CBSA has started its own investigation into the men's status.
Surrey has seen a number of shootings at homes and businesses over the last several months, but there's been an escalation since the new year.





