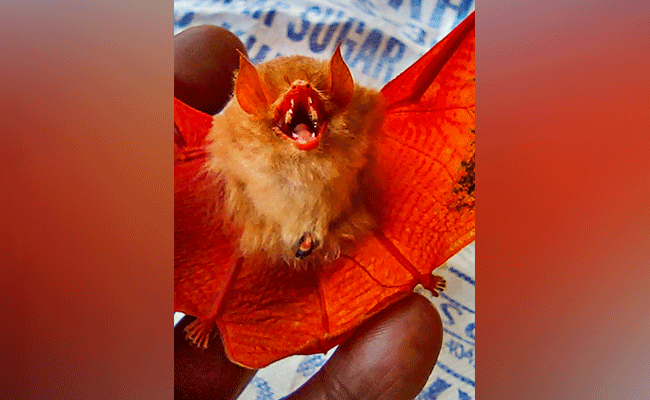
Jagdalpur (PTI): A rare orange coloured bat, which is a "near threatened" species, has been spotted in Chhattisgarh's Kanger Valley National Park, officials said on Wednesday.
The animal, also known as 'painted bat' and characterised by bright orange and black wings, was sighted at a banana farm in Parali Bodal village of the park on Monday, the national park's director, Dhammshil Ganvir, told PTI.
The bright orange-coloured bat was seen for the third time in the last few years in the Kanger Valley National Park located in Bastar district, he said, adding that earlier it was seen in 2020 and 2022.
The national park is famous for its limestone caves which also provide a suitable habitat for the bats, as per experts.
The painted bat, whose scientific name is 'Kerivoula picta', is a "near threatened" species and commonly seen in Bangladesh, Myanmar, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Vietnam, Ganvir said.
"The painted bats are aerial hawkers, which means they catch insects while flying in the air. It is often observed at the time of maize harvest," Ganvir said.
A survey will soon be conducted to ascertain varieties of bats found in the national park, he said.
The park, spread over an area about 200 sq km, is rich in biodiversity and sightings of some of the rare species of fauna were reported multiple times in the past, Ganvir said.
"In India, this bat has so far been seen in the Western Ghats, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha and the Kanger Valley in Chhattisgarh," he said.
These bats prefer to live in dry areas and dense moist forests. For roosting, they prefer to take shelter under banana leaves, the official said.
"We have decided to launch a survey to ascertain the varieties of bats found in the park and take conservation measures accordingly," he added.
Bastar-based ornithologist Ravi Naidu told PTI that the painted bat was first found in the Kanger Valley National Park in an injured condition in November 2020.
"We rescued it and later released it into its habitat," said the expert, who is currently working for the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) on a project.
Naidu's said his research paper on the painted bat in Kanger Valley was published in the Journal of the Wildlife Preservation Society 'Cheetal' in 2020.
The expert claimed he has spotted 26 species of bats in Chhattisgarh and said his research paper on it will be published soon.
The painted bat is characterised by bright orange and black wings, dense orange fur on the back and warm buff below. Their hairy face has no ornamentation or nose leaf. Their ears are large and funnel-shaped with transparent tragus, he said.
In India, there are about 131 species of bats and 31 of them are found in central parts of the country. The Kanger Valley National Park is famous for its limestone caves which also provide a suitable habitat for the bats, Naidu said.
During a faunistic diversity survey earlier, 20 species of bats were reported from Bastar district, mostly in the Kanger Valley, he added.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
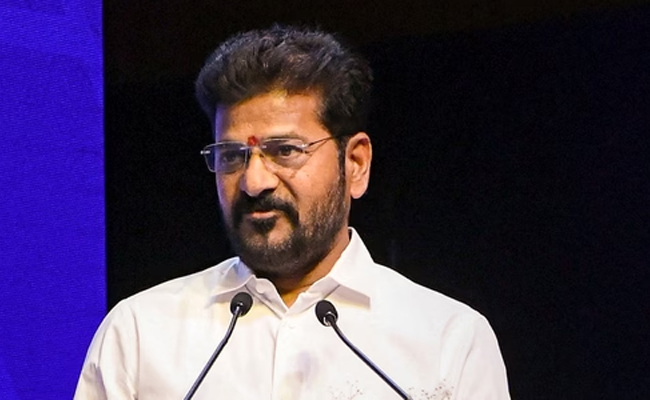
Hyderabad (PTI): Telangana Chief Minister A Revanth Reddy met Union Home Minister Amit Shah in Delhi on Wednesday night and urged him to increase the sanctioned strength of IPS officers to the state in view of its growing administrative and security needs.
The two leaders also discussed the recent surrender of several senior Maoist leaders before the Telangana Police and other issues.
"During the meeting, the two leaders discussed the issue of Maoist surrenders and their rehabilitation. The chief minister informed Shah that significant improvements in policing have taken place in Telangana over the past two years," an official release here said.
Highlighting that 591 Maoists have laid down their arms and joined the mainstream of society during this period, the chief minister said the state government was providing them compensation and rehabilitation assistance as per the rules.
He requested the Union home minister to extend financial support from the central government for development works in the backward regions of the state.
Reddy also urged Shah to increase the sanctioned strength of IPS officers to the state from 83 to 105 in line with the state's growing administrative and security needs, the statement said.
The first cadre review after the formation of Telangana was conducted in 2016, while the next review, due in 2021, was delayed and finally carried out in 2025. Even then, only seven additional IPS officers were allocated to the state, the chief minister informed Shah and requested that the third cadre review be conducted in 2026 as per the schedule.
Reddy explained that Telangana, like the rest of the country, is facing several modern challenges, including cybercrime, drug trafficking, white-collar crimes, and other emerging security threats.
He highlighted the reorganisation of the Hyderabad, Cyberabad, and Malkajgiri Police Commissionerates, the proposed formation of the Future City Commissionerate and the rapidly growing population in Hyderabad to underline the increasing administrative requirements of the state.