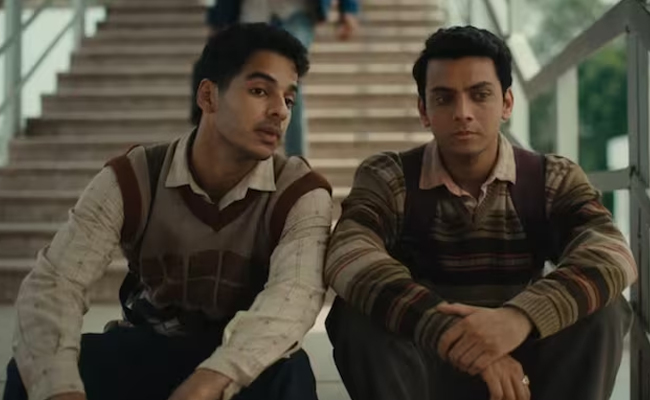Ahmedabad: A video of Justice Nirzar S Desai of the Gujarat High Court sharply questioning the state government over the legality of prohibiting videography inside police stations has gone viral on social media, reigniting the debate on citizens' rights and police accountability.
In a pointed exchange during court proceedings, Justice Desai asked the state’s lawyer:
"Tell me under which section videography is prohibited. Today we are living in an era of transparency. Assuming police are doing something illegal and a citizen intends to videograph it – which provision of law empowers you to stop someone from taking videography? Under which provision of law have you stopped the accused from video recording?"
The video has sparked widespread public interest, especially in the context of earlier legal interpretations around filming inside police premises.
View this post on Instagram
Background: Courts on videography in police stations
The question of whether video recording inside a police station is a punishable offence has previously been addressed by the Bombay High Court. In Ravindra Shitalrao Upadyay v. State of Maharashtra (2022 SCC OnLine Bom 2015), the Aurangabad bench ruled that such recording does not fall under Section 3 of the Official Secrets Act, 1923, which deals with spying. The court noted that police stations are not categorized as "prohibited places" under Section 2(8) of the Act. Therefore, secretly recording inside a police station cannot be treated as an offence under the Official Secrets Act.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Mumbai (PTI): Neeraj Ghaywan's much acclaimed "Homebound" is among the 15 films shortlisted in the best international feature category at the Oscars, moving a step close to the final five nominations and maybe a win.
The movie, inspired by a true story that became the basis of a news article during the pandemic, has been creating a global buzz since its debut in the Un Certain Regard category at the Cannes Film Festival this May.
Hollywood legend Martin Scorsese is a fan and has come onboard as an executive producer ahead of the award season.
Produced by Karan Johar and Adar Poonawalla, and starring Ishaan Khatter, Vishal Jethwa and Janhvi Kapoor, "Homebound" is Ghaywan's second movie after "Masaan".
"Homebound" will compete for an Oscar nomination alongside Argentina's “Belén”, Brazil's “The Secret Agent”, French drama "It Was Just an Accident”, Germany's "Sound of Falling” and Iraq's "The President's Cake".
ALSO READ: Actress Shilpa Shetty's restaurant booked for breaching operating hours
The other movies in the shortlist include Japan's “Kokuho”, Jordan's “All That’s Left of You”, Norway's “Sentimental Value”, Palestine's “Palestine 36”, South Korean hit “No Other Choice”, Spain's “Sirat”, "Late Shift" from Switzerland, “Left-Handed Girl”from Taiwan and Tunisian drama “The Voice of Hind Rajab”, the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences announced in a release on Tuesday.
The award for best foreign film, now re-categorised as best international feature, has so far eluded India.
Only three Indian films have received nominations in the category -- Mehmood Khan’s “Mother India”, Mira Nair’s “Salaam Bombay” and Ashutosh Gowarikar’s “Lagaan”. Deepa Mehta’s “Water”, starring John Abraham and Lisa Ray, also received a nomination but it was submitted from Canada.
Gujarati film "Chhello Show" in 2023 was the last film to get shortlisted.
Costume designer Bhanu Athaiya was the first Indian to get an Oscar, bagging the coveted prize in 1983 for the film "Gandhi". Other than her, A R Rahman, Resul Pukootty and M M Keeravani have also won individual Oscars.
Team "Homebound" celebrated the shortlist news with posts on social media.
"We made the shortlist... Way to go team Homebound'!" Johar shared in Instagram Stories.
In a post, the producer said it was difficult for him to articulate how "proud and elated" he was with the news.
"All of us @dharmamovies are privileged to have this proud and important film in our filmography... thank you @neeraj.ghaywan for making so many dreams of ours come true... from Cannes to being on the Oscar shortlist this has been such an overwhelming journey! Love to the entire cast and crew and teams of this special special film! Upwards and onwards...."
Ghaywan also shared the news on X.
"#Homebound has been shortlisted for Best International Feature Film at the 98th Academy Awards! We are deeply grateful for the extraordinary love and support we've received from around the world," he wrote on X with a special poster of the film.
Jethwa, who plays one of the two friends in the story opposite Ishaan Khatter, said the moment feels "surreal and incredibly humbling".
"To see 'Homebound' being shortlisted and progressing towards the Oscars is something I could have only dreamed of. I am deeply grateful for the love and support the film has received from audiences around the world," he said as he acknowledged Johar, Ghaywan and co-star Khatter and the rest of the team.
Khatter also shared the news on his Instagram stories and wrote, "Oscar ab dur nahi".
ALSO READ: MGNREGA rename: Gandhi made ‘Raghupati Raghav Raja Ram’ national anthem, Kangana sparks row
"Homebound" is inspired by journalist Basharat Peer's The New York Times article “Taking Amrit Home”, also titled "A Friendship, a Pandemic and a Death Beside the Highway".
The film portrays the childhood friendship between a Muslim and Dalit who chase a police job that promises them the dignity they have long been denied due to their surnames.
The Academy on Tuesday also announced shortlists in 11 other categories, including the newly added casting Oscars, animated shorts, cinematography, documentary feature, documentary short, original score and song, sound and visual effects categories.
Nominations for the 98th Academy Awards will be announced on Thursday, January 22, 2026.
Twenty-four categories will be awarded at the 98th Oscars. Each category has five nominees, except for best picture, which has 10.
The 98th Oscars will be held on Sunday, March 15, 2026, at the Dolby Theatre in Los Angeles.