New Delhi: The Government of Pakistan’s official X (formerly Twitter) handle has been withheld in India following the recent terrorist attack in Jammu and Kashmir’s Pahalgam that claimed 28 lives. The account, @GovtofPakistan, is no longer accessible within Indian territory and displays a message citing legal action as the reason for the restriction.
The move came shortly after India imposed a series of diplomatic sanctions against Pakistan, accusing it of supporting cross-border terrorism. The sanctions were announced by Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri following a meeting of the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
The CCS meeting was convened in the aftermath of the April 22 terror attack, in which a group of armed terrorists opened fire on tourists at Baisaran meadows in Pahalgam. According to officials, the attackers targeted Hindu pilgrims. The government has described the incident as a deliberate and ghastly act of violence.
India’s diplomatic response includes the following measures:
1. The Indus Waters Treaty of 1960 has been suspended until Pakistan provides credible and irreversible assurances that it will cease supporting terrorism.
2. The Attari Integrated Check Post has been closed for cross-border movement. Indian nationals with valid endorsements may return through this route until May 1, 2025.
3. The SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) has been revoked for Pakistani nationals. Existing SVES visas have been cancelled, and Pakistani nationals currently in India under this scheme must leave within 48 hours.
4. Defence, Naval, and Air Advisors at the Pakistani High Commission in New Delhi have been declared persona non grata and must leave the country within a week.
5. India is withdrawing its own Defence, Naval, and Air Advisors from its High Commission in Islamabad, rendering these posts inactive on both sides.
The Ministry of External Affairs stated that these measures reflect India’s firm stance against terrorism and its intent to safeguard national security. The government has reiterated its commitment to ensuring accountability for the attack and justice for the victims.
No official response has been issued by the Pakistani government regarding the withholding of its X handle or the sanctions announced by India.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
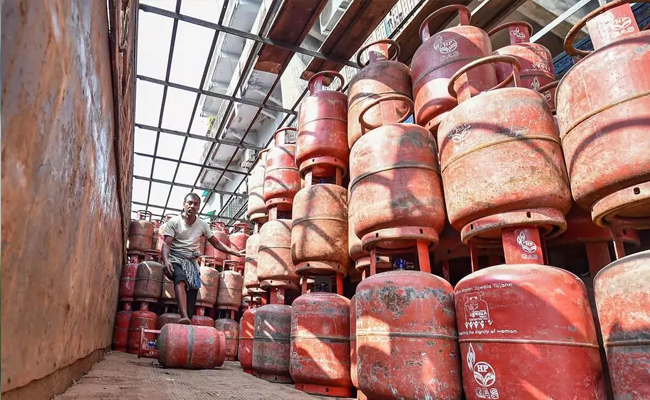
Thane (PTI): Authorities have seized illegally stored 1,839 gas cylinders and seven vehicles worth over Rs 67 lakh in the Dombivli MIDC area of Thane district, officials said on Saturday.
A special vigilance team of the Mumbai Rationing Department detected an illegal storage of domestic and commercial LPG cylinders in Phase-2 of Dombivli (East).
Cylinders belonging to multiple gas agencies were found stockpiled in closed vehicles, unauthorised warehouses, and open sheds without mandatory permissions from the Explosives Department, Fire Department, or oil companies, according to an official release.