New Delhi, Sep 4 : The long-drawn negotiations for the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement will continue into 2019 to sort out issues related to goods and services trade among member nations, Commerce Minister Suresh Prabhu said on Tuesday.
The Minister was briefing reporters here following a meeting of trade Ministers of the 16-nation RCEP in Singapore last week, which concluded on Sunday.
The RCEP is being negotiated by 10 Asean nations -- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, the Philippines, Laos and Vietnam -- and their six free trade agreement (FTA) partners India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
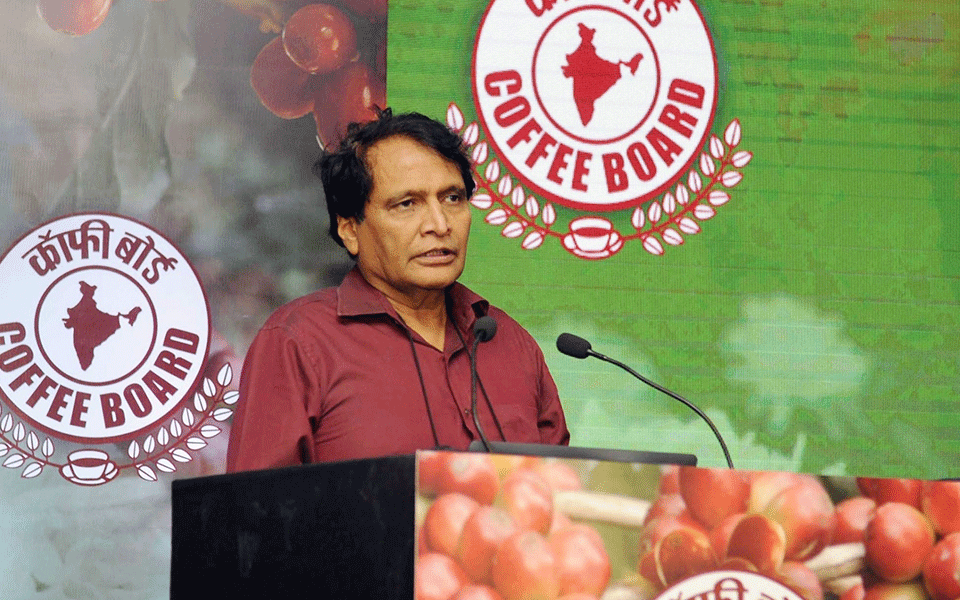
"The RCEP negotiations will not end in 2018. It has been agreed at the level of leaders that it will go on in 2019 as well. We will have the opportunity to work on all the issues," Prabhu said on the sidelines of a promotional event organised by the India Coffee Board.
Of the 16 countries in the proposed multilateral grouping, India does not have FTAs with Australia, New Zealand and China, which pose a hurdle to RCEP negotiations, Prabhu said.
"We cannot negotiate through the RCEP route with these countries... on India's insistence, we will now negotiate with China, Australia and New Zealand separately along with RCEP negotiations."
At the Singapore talks, India was able to convince on the issue of a grace period of more than 20 years before the RCEP guidelines on free trade are implemented, Prabhu said.
He said that custom lines being negotiated would be adopted later after suggestions are received by the Commerce Ministry from all trade associations in the country.
According to the Minister, at the Singapore meeting, India emphasised on three important issues, including linkage of services to goods negotiations since the agreement is a comprehensive one.
"We have emphasised on the inclusion of services under goods in the economic agreement. Our argument has been accepted and now services will also be included under the ambit of RCEP," he said.
India currently has a massive trade deficit with China, while segments of Indian industry have periodically voiced concern that lowering or eliminating import duties for China may flood the Indian markets with goods from the communist country.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
New Delhi (PTI): Leaders from Ladakh on Saturday welcomed climate activist Sonam Wangchuk's release from Jodhpur jail and demanded the release of remaining detainees.
Wangchuk was released from prison on Saturday after the Union government revoked his detention with immediate effect.
Ladakh MP Mohamad Hanifa hailed his release and urged the government to accept their demands for statehood and protection under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
"We welcome the release of Sonam Wangchuk. But others also need to be released, and the government should also take back the cases filed against people who participated in the protests," Hanifa told PTI.
The Union Home Ministry, in its statement, commented on the law and order situation in the Union Territory.
"... prevailing atmosphere of bandhs and protests has been detrimental to the peace-loving character of the society and has adversely affected various sections of the community, including students, job aspirants, businesses, tour operators and tourists and overall economy," it said.
Hanifa, however, said protest is a Constitutional right, and urged the government to resolve the issue through dialogue.
"If our voice is not heard in any other way, then there is another way to protest. We have always protested peacefully from day one, and we believe in peaceful protests. This is to make our voice reach the government," he said.
"We have always said that we want a solution to these issues through dialogue," he said.
Kargil-based politician and Kargil Democratic Alliance (KDA) member Sajjad Kargili, in a post on X, demanded the immediate release of Deldan Namgial and Smanla Dorjey, and appealed to the government to drop all charges against other detainees unconditionally.
"The revocation of NSA against Shri Sonam Wangchuk is a welcome move. However, our struggle of our legitimate rights continues," he said.
Wangchuk was detained on September 26, 2025, two days after protests over demands for statehood for Ladakh and its inclusion under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution rocked Leh.
More than 45 people, including 22 policemen, were injured in the protests.