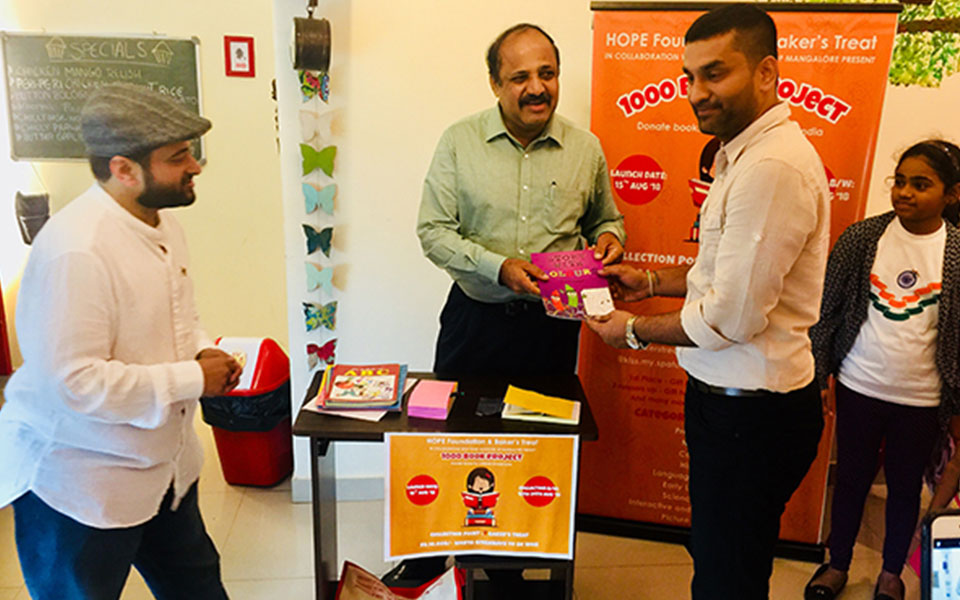
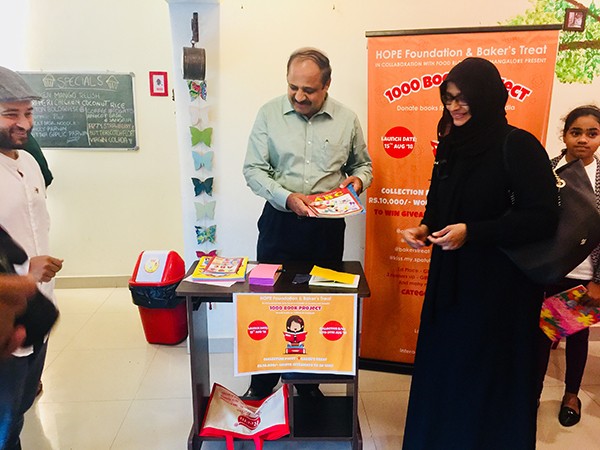
Mangaluru : Social service organisation HOPE Foundation and Bakers Treat Mangaluru in collaboration with some Food Bloggers has launched a unique initiative '1000 Book Project' with the slogan Jab Padega India tho Badega India on Wednesday . The idea of this project is to collect books from donors and send it to rural schools in India.
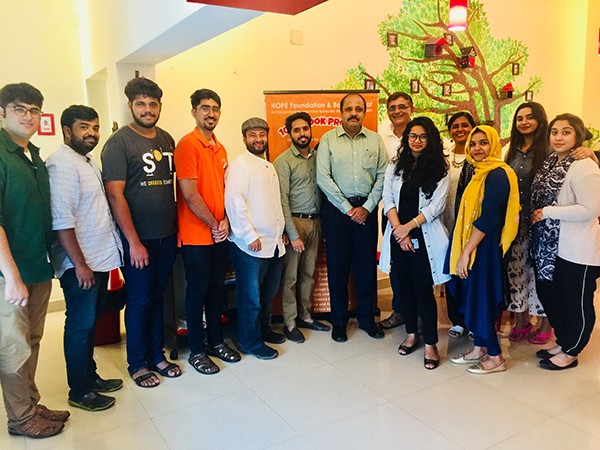
Popular Instagram bloggers from Mangalore like @thehungerqueen @thefatchickdiary @kiss.my.spatula @artbyfayaz @atu.pai @thejquest @bakerstreat and @traveller_soul_ixe joined in together and came up with this idea to celebrate the 72nd Independence Day of India.
Mr. T Suresh, Commissioner of Police, Mangaluru launched the project at Bakers Treat Cafe, Falnir on 15th August, 2018 at 5:30 PM. Few selected guests and book lovers of Mangaluru attended this event.
The first few books were accepted by The Top Cop of Mangaluru Mr T Suresh.
Mr T Suresh, Commissioner of Police addressed the gathering and appreciated the work that HOPE Foundation was doing and wished them the best.
Mr. Seif Sultan , Chairman of HOPE; thanked everyone for supporting the “ 1000 Book Project” and requested more people to join in and donate books to this movement which will support the poor children in all the 4 corners of India. He also mentioned that the people could donate cash for this project.
People can donate books until the 24th of August, 2018 at Baker’s Treat and stand a chance to win gift vouchers worth rupees 10,000.
Mrs. Mariam Mohiudeen of Baker’s Treat; and her husband Mr. Dean Mohiudeen along with their two sons Nedal and Nadeem handed over a gift of appreciation to Mr. T Suresh.
The guests included Mrs. Haseena Naufal, Mr. Viraj Hegde, Mr. Shareef Valal, Ms. Shreya Rao , Mr. Abdullah and many more.Trustee of HOPE Foundation Mr Najeeb was also present.
To know more follow the instagrammers mentioned above.





Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Thiruvananthapuram (PTI): A drone designed to tranquilise violent elephants without close human contact, recently unveiled by Vice President C P Radhakrishnan, marks a significant milestone in the use of indigenous UAV technology for human-wildlife conflict mitigation, the manufacturing company said.
The unveiling of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) took place on Sunday in the presence of Kerala Governor Rajendra Vishwanath Arlekar and Union Minister of State for Petroleum, Natural Gas and Tourism Suresh Gopi, underscoring the national importance of integrating advanced aerial systems into wildlife protection efforts, the company said in a release.
"The customised drone is engineered to support safe and precise elephant darting operations by enabling aerial-assisted tranquilisation with enhanced accuracy.
ALSO READ: Thousands of women offer pongala at Attukal Bhagavathy temple
"The system significantly reduces on-ground risk to forest personnel, minimises disturbance to wildlife, and improves operational efficiency during critical interventions involving distressed or conflict-prone elephants," it said.
It further said that nearly a decade ago, the platform marked the first drone designed by Garuda Aerospace for the Tamil Nadu Forest Department.
"The latest customised solution represents the culmination of years of field learning, technological upgrades, and mission-focused research and development," it said.
It also said that in the past, Garuda Aerospace has supplied multiple drones to leading conservation bodies, including the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), along with several forest departments across India.
"These deployments have supported wildlife monitoring, anti-poaching operations, habitat mapping, and rapid-response missions in ecologically sensitive regions," the release said.
Speaking on the occasion, Agnishwar Jayaprakash, Founder and Director of Garuda Aerospace, said that witnessing the Vice President unveil an evolved, customised solution for drone-aided elephant darting was "deeply fulfilling".
"Our journey has been built on incremental innovation—continuously enhancing our technology to responsibly serve wildlife conservation. We remain committed to creating indigenous solutions that protect both animals and communities," he was quoted as saying.
As India continues to address the growing challenges of human-elephant conflict, drone-assisted darting offers a safer, more efficient, and humane alternative to traditional ground-based approaches, Garuda Aerospace, a drone tech start-up, has said.