Bengaluru: The Karnataka State Pollution Control Board (KSPCB) on Friday said they will be analyzing their city action plans using two recent air pollution source assessment studies in their efforts to improve air quality across the state.
While Bengaluru's deteriorating air quality is a cause for concern, studies released by the Center for Study of Science, Technology, and Policy (CSTEP) have revealed that measures targeted at polluting sources can help lower pollution levels.
According to CSTEP’s research released earlier this year, the transportation industry is the largest source (40–51%) of particulate matter, followed by road dust resuspension (17–51%). Construction dust, household gasoline, and diesel generators are among the other polluting industries.
Air has suspended particulate matter (PM) of different sizes. Many of these are a complex mixture of dust, pollen, soot, and smoke and they are hazardous. Of this, PM 2.5 is the smaller kind, with a diameter, of not more than 2.5 micrometers (fine particles). PM2.5 is considered to have a very significant health impact as it can stay in the air for days or weeks, and is small enough to invade the lung airways.
The studies, titled "Emission Inventory and Pollution Reduction Strategies for Bengaluru" and "Identification of Polluting Sources for Bengaluru," identified polluting sources/activities or hotspots for the city, which has been a major concern for air pollution regulators and policymakers.
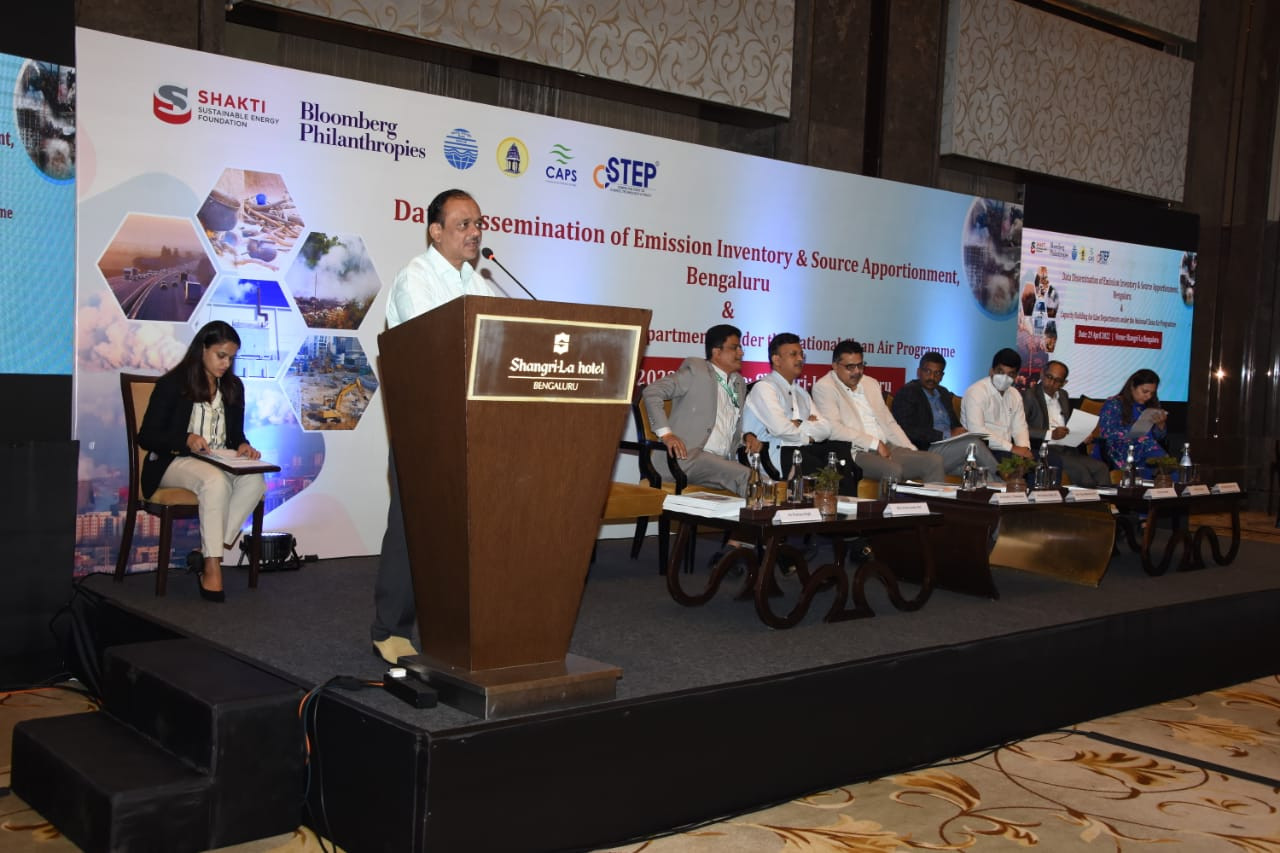
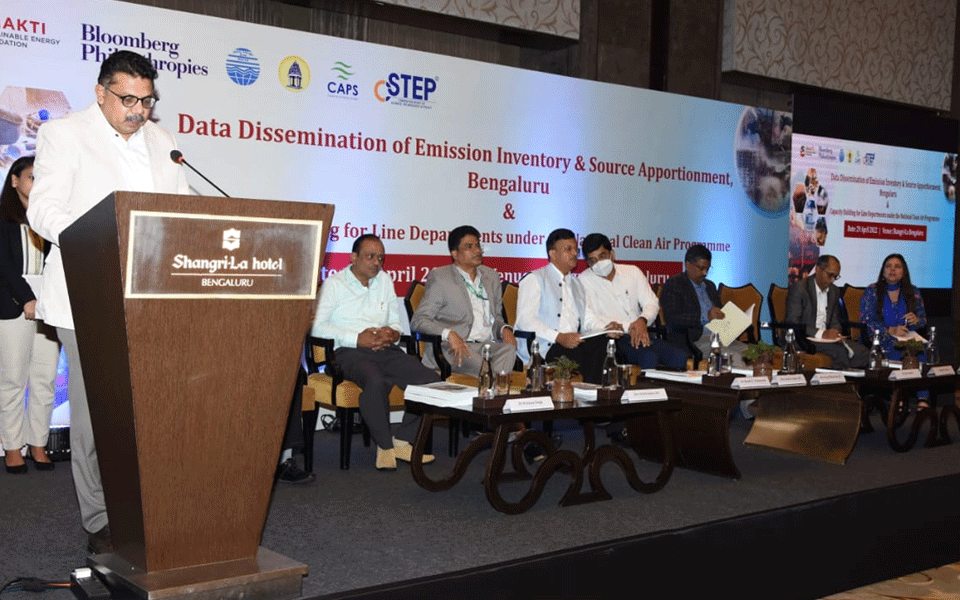
On Friday, April 29, 2022, CSTEP held data dissemination and capacity building event for over 50 Karnataka government officials at Shangri-La, Bengaluru, where findings of the two studies were shared to ensure the implementation of solutions from the studies as well as empower government officials to make informed decisions.
At the workshop, Dr Shanth A. Thimmaiah, Chairman, KSPCB reflected on the need for micro action plans that will help pollution control boards to take effective, result-oriented action toward improving air quality. “The event is an opportunity to evaluate our work. CSTEP’s reports will be used as a base for studying and making clean air action plans for three other non-attainment cities through a Plan-Do-Check-Act approach,” he said.
Shri Vijay Mohan Raj, IFS, Principal Secretary, Ecology and Environment Department, Government of Karnataka, highlighted the need for air guilt—the guilt that comes from knowing that we are contributing to air pollution (and how)—to be felt by all and drive our actions. “To do this, data needs to be presented in simple formats that could be understood even by children. I hope that such reports can bring about last-mile changes to improve air quality,” he said.
CSTEP’s study findings revealed that Bengaluru can see possible concentration reductions of approximately 26.5%, ~13.5%, and ~9.6%, respectively, for high-, medium-, and low-emission reduction scenarios (measures clubbed with varying levels of compliance) for both PM10 and PM2.5 by 2024.
Key measures considered under the scenarios were improvement in public transportation infrastructure, diesel particulate filter installation in trucks, and a strict blanket ban on open waste burning. “Considering Bengaluru’s status as a non-attainment city, conducting a scientific assessment through source apportionment and emission inventory was crucial towards preparing efficient strategies,” said Dr. Pratima Singh, Research Scientist at CSTEP who led the study.




CSTEP—as an Institute of Repute under the National Clean Air Programme—is working with the KSPCB and Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) to help implement the recommendations. By training state government officials to use scientific methods to assess air quality through this event, CSTEP hopes to enhance the quality and effectiveness of policy decisions.
Ms Puja Tewary, India Coordinator, Climate and Environment Programs, Bloomberg Philanthropies, said, “Scientific evidence highlighted in the report could inform both line departments and KSPCB in preparing city micro action plans.” She reiterated that mutual collaborations among organizations are essential.
A ‘meaningful’ action plan could be prepared as a result of CSTEP’s studies, said Shri Gaurav Gupta, IAS, Chief Commissioner, Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP). “The studies highlight vehicular pollution and road dust as the main issues for Bengaluru. We are working on these sectors. Bengaluru is among the fastest-growing cities, and this is the main reason for air pollution,” he added.
Readers can access the study reports at https://cstep.in/publications.php
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Tehran: Iran has reportedly declared 40 days of public mourning following the killing of the country’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, Al Jazeera reported citing Iranian state media.
According to the report, Fars News Agency said the Iranian government has announced 40 days of nationwide mourning in the wake of Khamenei’s killing. The agency also reported that seven days of public holidays have been declared.
Further updates are awaited.


_vb_68.jpeg)

