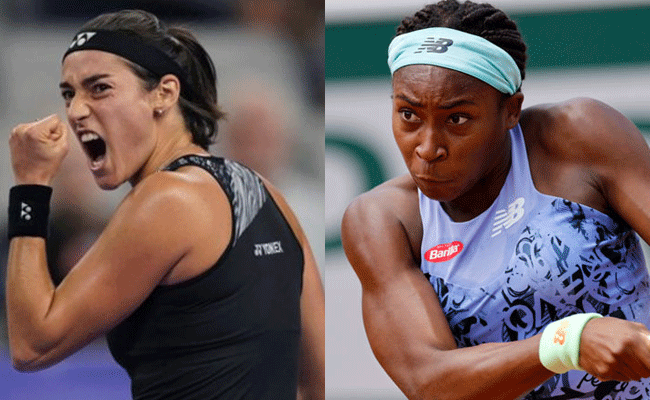Melbourne (AP): It all came so seemingly easy for Iga Swiatek last season two Grand Slam trophies, eight titles overall, a 37-match winning streak, a lengthy stay at No. 1 in the rankings.
Those accomplishments made everyone else expect constant greatness from Swiatek, which she can't do anything about. They also changed the way she approached big moments, and a 6-4, 6-4 loss to Wimbledon champion Elena Rybakina in the Australian Open's fourth round Sunday made Swiatek wonder whether she needs to reassess her outlook.
"I felt like I took a step back in terms of how I approach these tournaments, and I maybe wanted it a little bit too hard. So I'm going to try to chill out a little bit more," Swiatek said. "I felt the pressure, and I felt that I don't want to lose' instead of I want to win.'"
So there will not be a showdown between Swiatek and No. 7 seed Coco Gauff in the quarterfinals at Melbourne Park. Instead, it will be Rybakina taking on 2017 French Open champion Jelena Ostapenko, a 7-5, 6-3 winner against Gauff, with a semifinal berth at stake.
"I kept her under so much pressure," Ostapenko said.
Both the 22nd-seeded Rybakina, a 23-year-old who represents Kazakhstan, and the 17th-seeded Ostapenko, a 25-year-old from Latvia, made it this far in Australia for the first time.
"There was moments in the match where I was getting frustrated, because I normally can problem-solve, but today I feel like I didn't have much answers to what she was doing," said Gauff, an 18-year-old from Florida who was the runner-up to Swiatek at the French Open last June.
"There was balls I was hitting deep, and she was hitting them on the line and hitting them back deep, over and over again," said Gauff, who wiped away tears during her news conference. "It's just one of those days that just didn't go my way and went her way."
One key: Ostapenko went 3-for-3 converting her break chances, and Gauff was just 1-for-8 in such situations.
Rybakina, meanwhile, used her big serve to produce a half-dozen aces, part of an overall 24-15 edge in total winners against Swiatek.
The women's fourth-rounders scheduled for later Sunday were: No. 3 Jessica Pegula vs. 2021 French Open champion Barbora Krejcikova, and two-time Australian Open champion Victoria Azarenka vs. unseeded Zhu Lin.
In men's action, 13th-seeded Karen Khachanov reached the quarterfinals by beating No. 31 Yoshihito Nishioka 6-0, 6-0, 7-6 (4), setting up a meeting against No. 10 Hubert Hurkacz or No. 29 Sebastian Korda, who were playing in the afternoon.
Other men's matches Sunday: No. 3 Stefanos Tsitsipas vs. No. 15 Jannik Sinner, and No. 6 Felix Auger-Aliassime vs. unseeded Jiri Lehecka.
Until Sunday, both Swiatek and Gauff looked fairly dominant for a week, winning every set they contested. Swiatek dropped a total of just 15 games, Gauff just 19, through three matches.
"For sure, when you play against No. 1, I think you have really nothing to lose. I knew that I had to be aggressive from the first ball because she's a great mover, and she defends really well," Rybakina said. "So I was trying to just attack her from the first ball, and it really worked well.
Her ranking of No. 25 does not properly reflect her ability or results because her championship at the All England Club in July did not come with any ranking points. The WTA and ATP tours withheld all points at Wimbledon in 2022 after the All England Club barred players from Russia and Belarus from participating because of the invasion of Ukraine.
Rybakina who was born in Moscow but has played for Kazakhstan since 2018, when that country offered her funding to support her tennis career said her current standing "doesn't bother me, because it's been already six months," yet also acknowledged it does provide some motivation.
Despite her status as a major champion, Rybakina has been out of the spotlight: Her first-round match at Melbourne Park was placed on tiny Court 13 last Monday; her match against two-time Slam champ Garbi e Muguruza at least year's U.S. Open was on Court 4.
But her game is worthy of much more attention, as she displayed in knocking out Swiatek, one match after defeating 2022 Australian Open runner-up Danielle Collins.
Swiatek was not at her best, and Rybakina had a lot to do with that. In the opening game, Swiatek led 40-love but got broken. In the next, Swiatek held two break points at 15-40 but failed to convert either. So early on, while it ended up being 2-2, it very well could have been 4-0 in Swiatek's favor, and she termed that sequence "a little bit disturbing."
Rybakina wound up serving out that set at love, capping it with a 113 mph (183 kph) ace, and her dangerous backhand was quite a help, too: She produced six winners off that wing in the first set, compared with zero for Swiatek.
In the second set, Swiatek appeared to have gotten herself back on track, going up 3-0. But that surge didn't last long, and Rybakina took six of the match's last seven games.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Singapore (PTI): An Indian-origin Malaysian man was sentenced in Singapore to 12 years' jail and 12 strokes of the cane for raping a domestic worker outside a train station after tricking her into thinking that he was a police officer.
Sharveen Chetty, 48, pleaded guilty on February 4 to one charge of raping the 35-year-old Indonesian woman in the bushes outside Exit F of a subway, Little India Mass Rapid Transit station, at about 8pm on July 11, 2022.
The victim was with her friends at the time, but Chetty lured her away before he sexually assaulted her, according to a report by The Straits Times on Thursday.
Two other charges – a second rape charge and a charge of impersonating a police officer – were taken into consideration during sentencing on Wednesday.
The witnesses who testified on the first day of the trial included a doctor from Women’s and Children’s Hospital who examined the victim a day after the rapes, and forensic scientists from the Health Sciences Authority.
Chetty had initially contested the charges in a High Court trial that began on February 3. But he changed his mind and pleaded guilty on what would have been the second day of the trial, according to the daily report.
In sentencing, Justice Dedar Singh Gill considered it aggravating that Chetty had targeted the victim because she was a foreigner who might be unfamiliar with the local authorities.
The judge rejected the defence's arguments that the rape was not premeditated.
The judge, however, noted that Chetty had pleaded guilty before the victim and key prosecution witnesses testified, thus sparing her and her friends from going through cross-examination.
The prosecution had sought a sentence of between 11 and 13 years’ jail and 12 strokes of the cane, noting Chetty’s extensive efforts to disguise himself, and his predatory act of leading the victim away from the rest of the group.
Chetty admitted that he became sexually attracted to the victim.