New Delhi, Dec 30: Rishabh Pant's plan to surprise his mother ahead of the new year turned into a horrific accident after his car collided with a road divider on the Delhi-Dehradun highway in the wee hours on Friday.
The star India wicket-keeper batter was lucky to survive serious injuries due to his alertness, jumping off his Mercedes in the nick of time as the car went up in flames after hitting the divider.
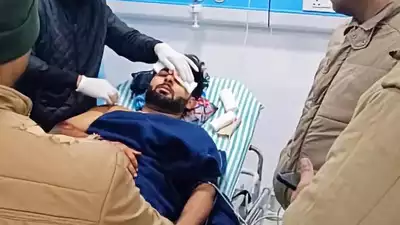
Dr. Sushil Nagar, who was the first to attend to Pant in the emergency ward of Saksham Hospital near Roorkee, said the cricketer didn't suffer any fracture but there was a ligament injury on his knee which would require further investigation.
"When he was brought to our hospital, he was fully conscious and I spoke to him. He wanted to surprise his mother and was going back home," Nagar told PTI.
He suffered big bruises on his back but Nagar said those are not burn injuries.
"The injuries happened because he jumped out of car by breaking the window of his car as soon as it caught fire. As he landed on the side of the road on his rear, the skin peeled off. But those are not burn injuries and not very serious."
The 25-year-old dozed off and lost control of his Mercedes early morning on Friday en route to his home in Roorkee. He was alone in the car.
The accident happened at Mohammadpur Jat in Manglaur town of Haridwar district.
He suffered injuries on his head, back and feet but is in a stable condition.
"He had two lacerations (blunt trauma) on his head but I didn't put stitches. I have recommended him to Max Hospital where a plastic surgeon might see him," Nagar said.
The doctor, however, said Pant suffered a ligament tear on his right knee and the extent of that injury can only be ascertained after an MRI scan.
"However reports of X Rays conducted at our hospital suggest that there are no bone injuries. Yes, there is a ligament tear on his right knee. How serious it is can only be detected after further investigation and detailed MRI," he said.
Ligament injuries have various grades and it can take 2 to 6 months to regain full fitness, which puts a serious question mark over Pant's availability for the home Test series against Australia, starting February 9.
Pant was not part of the upcoming white-ball series against Sri Lanka beginning on January 3. He was supposed to join the National Cricket Academy (NCA) in Bengaluru for a strength and conditioning programme ahead of February's Border Gavaskar Trophy.
The explosive left-handed wicket-keeper batter has scored 2,271 runs in 33 Tests so far with the help of five hundreds and 11 half-centuries. He has also represented the country in 30 ODIs and 66 T20Is, scoring 865 and 987 runs respectively.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
New Delhi: The Supreme Court has granted bail to Congress MLA Vinay Kulkarni in connection with the murder of BJP Zilla Panchayat member Yogish Gowda from Hebballi in Dharwad district.
A bench headed by Justice Sanjay Karol passed the order granting bail to Kulkarni.
Earlier, following the cancellation of his bail, Kulkarni had surrendered before the Special Court for MPs and MLAs. His recent bail plea had also been rejected by the High Court.
Subsequently, Kulkarni approached the Supreme Court, which has now granted him bail.