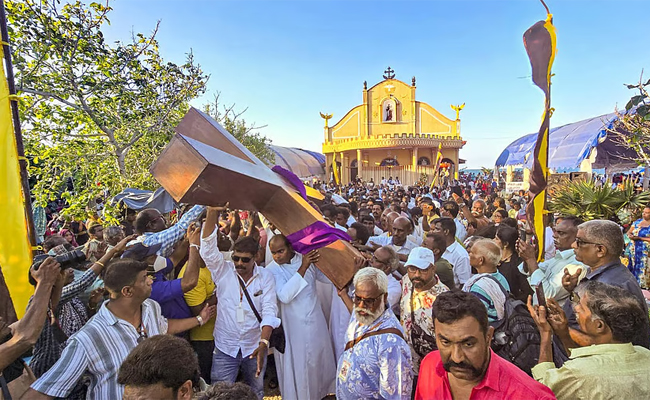Sydney (PTI): Former Australia skipper Steve Smith says his team is better off training on its own rather than playing tour games on "irrelevant" Indian pitches ahead of the four-Test Border-Gavaskar series.
Australia have decided not to play a single tour game in India during the month-long Test series, primarily due to the hosts serving up green tops for practice matches and spinning tracks for the actual games.
Smith, who won the country's best men's player award for the fourth time in his career on Monday, said nets sessions would benefit his side more than the tour games.
The 18-member squad, led by Pat Cummins, had a pre-series camp on spin-friendly tracks in Sydney and will have a week-long stint in Bengaluru before the first Test in Nagpur from February 9.
"We normally have two tour games over in England. This time we don't have a tour game in India," Smith was quoted as saying by news.com.au on Monday ahead of the team's departure to India.
"The last time we went (to India) I'm pretty sure we got served up a green top (to practice on) and it was sort of irrelevant. Hopefully, we get really good training facilities where the ball is likely to do what it's likely to do out in the middle, and we can get our practice in," said Smith, who beat Travis Head and David Warner to win the Allan Border medal on Monday.
Australia have been criticised for not including tour games, which are an integral part of a long series, in their itinerary. But Smith said rigorous nets sessions will help spinners train better.
"We're better off having our own nets and getting spinners in and bowling as much as they can."
Smith, whose side had lost the series 1-2 when it toured India in 2017, indicated a lot of thinking had into the decision.
"We'll wait and see when we hit the ground. I think we've made the right decision to not play a tour match. Like I said, last time they dished up a green top for us (in a tour game) and we barely faced any spin, so it's kind of irrelevant."
The Australians had a training session in Sydney last week on pitches that had significant cracks to replicate Indian conditions.
"It's (the Test series in India) certainly huge. I don't know if it's (winning in India) the final frontier. I've never won there, I've been there twice (for Tests), it's always difficult playing there. We've got some challenges in front of us, but the guys are ready for it," added Smith.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Rameswaram (Tamil Nadu) (PTI): Nearly 4,000 Indian pilgrims on Friday set sail for the uninhabited Katchatheevu islet to participate in the annual two-day festival, which will officially commence at 4 pm at the St Antony’s Church, officials said.
The festival marks a significant moment of shared cultural and religious heritage between India and Sri Lanka.
The first batch of devotees was flagged off from the Rameswaram fishing harbour at approximately 6 am by Ramanathapuram District Collector Simranjeet Singh Kahlon.
ALSO READ: Explosions and aircraft sounds heard in Kabul, hours after Afghanistan attacks Pakistan
According to official records, a total of 3,996 registered pilgrims -- comprising 3,033 men, 726 women, and 150 children -- are crossing the Palk Strait in a fleet of 118 boats, which includes 92 mechanised trawlers and 26 country boats.
The festival will officially commence with a traditional flag-hoisting ceremony. This will be followed by the 'Way of the Cross' procession and a late-night chariot festival, where the statue of the patron saint will be carried around the shrine by Sri Lankan Navy personnel, sources said.
Strict security measures are in place, with the Indian Coast Guard and Customs department conducting a three-tier verification process at the Rameswaram jetty. All pilgrims were required to produce their Aadhaar cards and a mandatory Police No Objection Certificate (NOC).
Authorities have strictly prohibited the carriage of plastic items, alcohol, and excessive jewellery.
According to official sources, all vessels are equipped with adequate life jackets and are being escorted by Coast Guard hovercrafts up to the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL).
The festivities will reach their peak on Saturday morning with a Special High Mass conducted by the Bishops of Jaffna and Colombo in both Tamil and Sinhala. The event will conclude with the lowering of the flag, after which the Indian pilgrims will begin their return journey.
To facilitate the event, the Tamil Nadu Fisheries Department has enforced a total fishing ban in the region until March 1, leaving over 1,000 local boats moored at the docks to ensure clear passage for the pilgrim fleet.
The islet was ceded to Sri Lanka by India by ways of two agreements in 1970s.