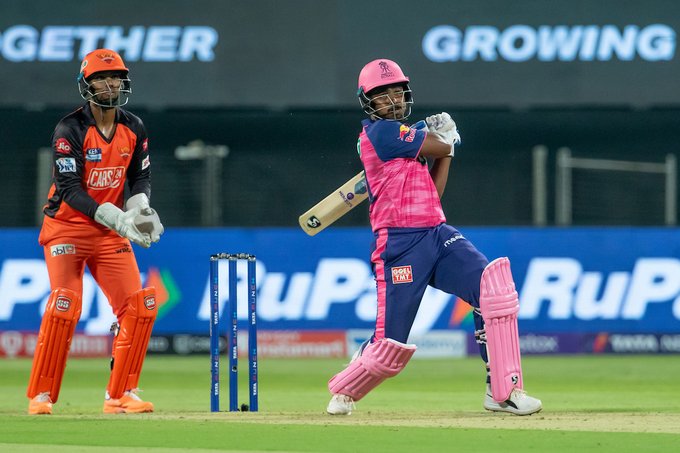
Pune, Mar 29: Skipper Sanju Samson led from the front with a scintillating 27-ball 55 as Rajasthan Royals posted an imposing 210 for six against Sunrisers Hydrabad in their Indian Premier League match here on Tuesday.
Samson and Devdutt Padikkal (41 off 29 balls; 4x4; 6x2) added 73 runs for the third wicket off 41 balls, before Shimron Hetmyer used his brute power to clobber 32 in only 13 deliveries and take RR past 200.
Samson's six-hitting prowess was on display as he struck five maximums and three boundaries, sparing no bowler during his entertaining stay in the middle.
Later Hetymar smashed three sixes.
Put into bat, Royals opener Jos Buttler, on zero, survived courtesy a no ball. Buttler (35) and Yashasvi Jaiswal (20) then gave the side a flying start, stitching a 58-run stand to lay the foundation for a big total.
Buttler was brutal on Umran Malik, hammering him for two fours and two maximums in the fourth over, as RR collected 21 runs.
The two openers then struck a six each off Washington Sundar (0/47) in the next over as RR raced to 52 for no loss after five overs.
Jaiswal however perished in the seventh over, holing out to Aiden Markram off Romario Shepherd. While Buttler, who hit three fours and as many sixes, was dismissed at the start of the ninth over as RR slipped to 75 for two.
Showing intent straightaway, Samson started with a four and a six over long-off and hit another maximum over fine-leg, as he took on the SRH attack with gusto.
While Samson found the fence at will, Padikkal too got into the groove and began attacking in the 12th over when he pulled T Natarajan for a maximum.
Samson was again brutal on Sundar, striking him for two successive sixes in the 16th over as RR marched on.
SRH removed Paddikkal and Samson in quick succession, but a lot of damage had been done by then, before Hetmyer compounded the bowling team's woes with his massive hits as RR scored 123 runs in the back 10.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
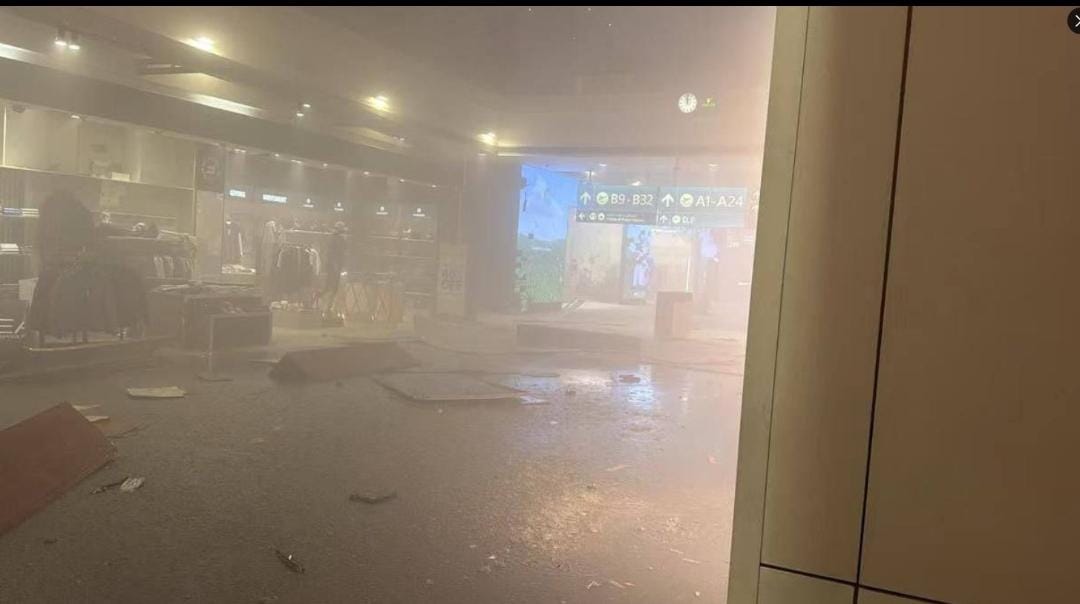
Dubai: Reports have emerged claiming that Dubai International Airport has been hit by a missile amid rising tensions in the region.
Several videos claiming to be that from the Dubai Airport were being circulated online.
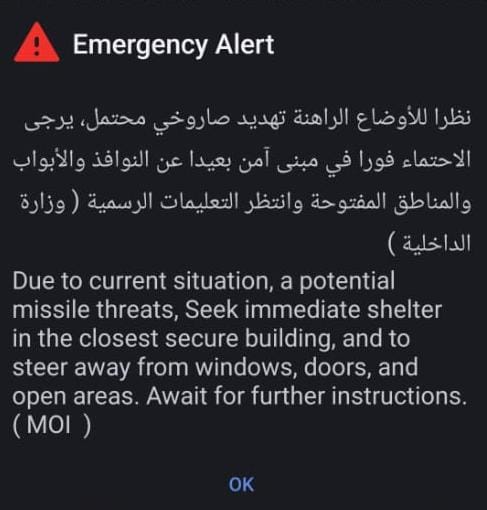
The claims surfaced shortly after emergency alerts were issued across the UAE warning residents and visitors of a potential missile threat and advising them to seek shelter.
However, there has been no official confirmation from UAE authorities regarding any strike on Dubai airport.
Details about possible damage or casualties remain unclear. Authorities are yet to release a formal statement on the reported incident.