Dubai: Indian Cricket Team Captain Virat Kohli on Thursday announced that he will step down as the captain of the Indian T20 side after the T20 World Cup in Dubai next month.
The Indian skipper took to his Twitter handle to break the news to his fans.
“After a lot of contemplation and discussion with my close people, Ravi bhai and also Rohit, who have been as essential part of the leadership group, I’ve decided to step down as the T20 captain after this T20 World Cup in Dubai in October” the post read.
He further added that he has spoken to the BCCI secretary Jay Shah and President Sourav Ganguly along with selectors about his decision.
“I have been fortunate enough to not only represent India but also lead the Indian Cricket Team to my utmost capability. I thank everyone who has supported me in my journey as the Captain of the Indian Cricket Team. I couldn’t have done it without them – the boys, the support staff, the selection committee, my coaches and each and every Indian who prayed for us to win” the post added.
The Indian captain added that the decision has come on the back of immense workload over the last 8-9 years playing all the three formats of the game and captaining regularly for last 5-6 years.
“I feel I need to give myself space to be fully ready to lead the Indian Team in Test and ODI Cricket. I have given everything to the Team during my time as T20 Captain and I will continue to do so for the T20 captain as a batsman moving forward” it added.
🇮🇳 ❤️ pic.twitter.com/Ds7okjhj9J
— Virat Kohli (@imVkohli) September 16, 2021
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Dubai/Abu Dhabi: Residents and visitors across the United Arab Emirates received a fresh emergency alert on their mobile phones stating that the situation in the country is currently safe.
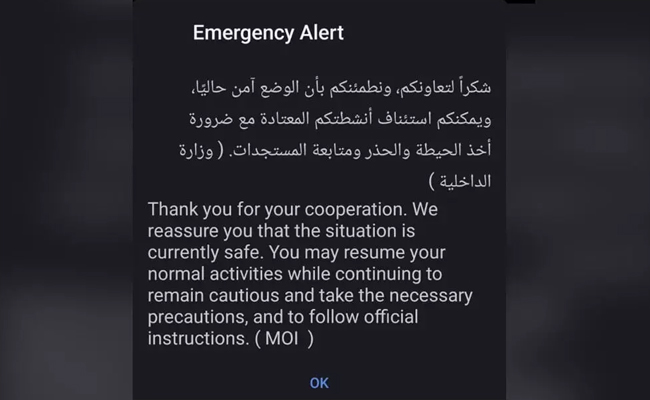
The message, issued by the Ministry of Interior (MOI), thanked people for their cooperation and reassured them that conditions were stable.
“Thank you for your cooperation. We reassure you that the situation is currently safe. You may resume your normal activities while continuing to remain cautious and take the necessary precautions, and to follow official instructions. (MOI),” the alert read.
The notification was sent in both Arabic and English through the country’s emergency alert system.
The advisory comes after earlier alerts warning of potential missile threats amid rising regional tensions. Authorities have urged the public to stay cautious and follow official guidance.