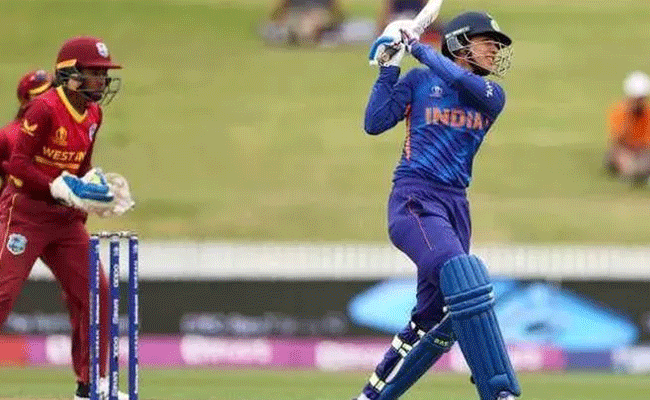
East London (South Africa) (PTI): Smriti Mandhana and captain Harmanpreet Kaur cracked fine unbeaten half-centuries as India defeated West Indies by 56 runs to keep their slate clean in the Women's T20I Tri-Series here.
India, after winning the toss and electing to bat, were off to a good start and managed 167 for two in 20 overs. They then restricted the opponents to 111 for four to eke out their second consecutive win of the series.
Openers Yastika Bhatia and Mandhana stitched together a 33-run partnership before the former was dismissed by off-spinner Karishma Ramharack for 18 with just one delivery remaining in power play.
Ramharack tossed the ball up outside off and Yastika attempted a drive over covers but ended up playing away from her body. A faint outside edge saw the opener give an easy catch to wicketkeeper Rashada Williams.
Her dismissal brought in Harleen Deol but her stay at the crease didn't last long, as she was trapped in front while trying to flick the ball on the off-side from pacer Shanika Bruce.
The early response to the length ball saw the young middle-order batter miss the stroke, with the ball hitting her on the front pad.
At 52 for two, there were some tense moments but once Mandhana and Harmanpreet paired up, boundaries flowed freely.
Harmanpreet, who was back leading the side after missing the opening match of the tri-series reportedly due to illness, was on song as she smashed a 35-ball 51 studded with eight boundaries.
Mandhana, after failing with the bat in the opening game against South Africa, was equally belligerent scoring 74 off just 51 deliveries as the duo batted together for nearly 12 overs to guide India to a competitive score.
Mandhana, who was dismissed for seven runs in the tri-series opener against South Africa Women, hit 10 boundaries and a six, even as the opponents utilised seven bowlers to break the partnership.
A target of 167 was always going to be a difficult chase and India spinners led by Radha Yadav throttled the runs, giving away precious little by way of loose deliveries. The 22-year-old Radha gave away just 10 runs in her four overs while also taking the wicket of Shemaine Campbelle (47), who consumed 57 deliveries.
By the time Campbelle was dismissed attempting a pull off a full toss but holing out to Amanjot Kaur at deep mid-wicket, the match was as good as lost for West Indies as they were 96 for four with just 15 deliveries remaining.
Skipper Hayley Matthews and Afy Fletcher too couldn't get the runs flowing and in the end a target of 167 proved too big to chase.
Brief scores: India Women 167 for 2 in 20 overs (Smriti Mandhana 74 n.o., Harmanpreet Kaur 56 n.o.) beat West Indies Women 111 for 4 in 20 overs (Shemaine Campbelle 47, Hayley Matthews 34 n.o.; Deepti Sharma 2/24, Radha Yadav 1/10) by 56 runs.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
Singapore (PTI): An Indian-origin Malaysian man was sentenced in Singapore to 12 years' jail and 12 strokes of the cane for raping a domestic worker outside a train station after tricking her into thinking that he was a police officer.
Sharveen Chetty, 48, pleaded guilty on February 4 to one charge of raping the 35-year-old Indonesian woman in the bushes outside Exit F of a subway, Little India Mass Rapid Transit station, at about 8pm on July 11, 2022.
The victim was with her friends at the time, but Chetty lured her away before he sexually assaulted her, according to a report by The Straits Times on Thursday.
Two other charges – a second rape charge and a charge of impersonating a police officer – were taken into consideration during sentencing on Wednesday.
The witnesses who testified on the first day of the trial included a doctor from Women’s and Children’s Hospital who examined the victim a day after the rapes, and forensic scientists from the Health Sciences Authority.
Chetty had initially contested the charges in a High Court trial that began on February 3. But he changed his mind and pleaded guilty on what would have been the second day of the trial, according to the daily report.
In sentencing, Justice Dedar Singh Gill considered it aggravating that Chetty had targeted the victim because she was a foreigner who might be unfamiliar with the local authorities.
The judge rejected the defence's arguments that the rape was not premeditated.
The judge, however, noted that Chetty had pleaded guilty before the victim and key prosecution witnesses testified, thus sparing her and her friends from going through cross-examination.
The prosecution had sought a sentence of between 11 and 13 years’ jail and 12 strokes of the cane, noting Chetty’s extensive efforts to disguise himself, and his predatory act of leading the victim away from the rest of the group.
Chetty admitted that he became sexually attracted to the victim.