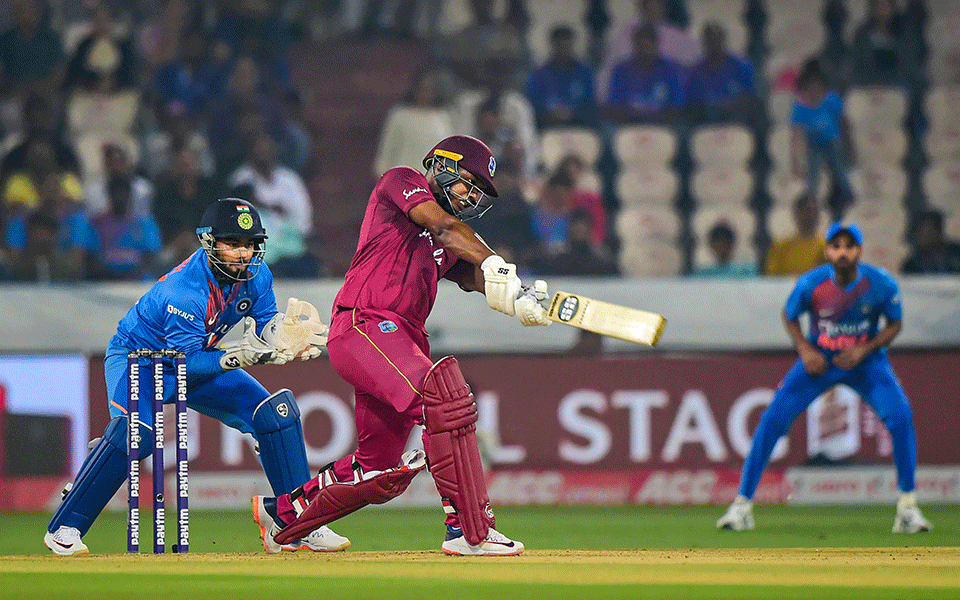
Hyderabad: Shimron Hetmyer struck a quick half-century as West Indies produced a fine batting display to post a challenging 207 for 5 against India in the first T20 International of the three-match series here on Friday.
An aggressive Hetmyer made 56 off 41 balls which was studded with two boundaries and four hits over the fence to hold West Indies from one end after being sent into bat.
He first added 37 runs with Brandon King (31 off 23 balls) and then shared 71 runs with skipper Kieron Pollard (37 off 19 balls) to lay the base for the West Indies total.
The Indians, however, were far from impressive on the field as Washington Sundar and Rohit Sharma dropped a few catches.
Off-spinner Washington Sundar (1/34) leaked runs in the first over before Deepak Chahar (1/56) gave India the breakthrough in the next over, taking the wicket of Lendl Simmons, caught by Rohit Sharma in the first slip.
Evin Lewis (40 off 17) and young King then added 51 runs for the second wicket, during which they played some fearless shots, to take West Indies forward.
Lewis, in particular, was the more aggressive of the two as he dispatched to the stands any bad delivery that came his way. He pulled Chahar for two sixes in the fourth over to make his intentions clear.
Lewis continued the onslaught and struck comeback man Bhuvneshwar Kumar for a six and a four in consecutive balls. He then smoked off-spinner Sundar over the cover boundary but perished in the next ball, LBW in search of one shot too many.
Young King and Hetmyer then added 37 runs for the third wicket before the former was stumped by Rishabh Pant off Ravindra Jadeja's (1/30) bowling.
Hetmyer, on the other hand, went about his business in a quiet fashion, hitting the bad deliveries out of the park to register his fifth half-century in T20 cricket in 35 balls.
But a double breakthrough by leg-spinner Yuzvendra Chahal (2/36) in the 18th over put a check on West Indies' scoring rate.
Hetmyer was the first to depart in the first delivery of the 18th over when he gave a simple catch to Rohit at deep backward square and then a ball later, Pollard was cleaned up by Chahal.
Jason Holder (24 not out off 9 balls) and Dinesh Ramdin (11 not out off 7) remained unbeaten as West Indies scored 63 runs off the last five overs.
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
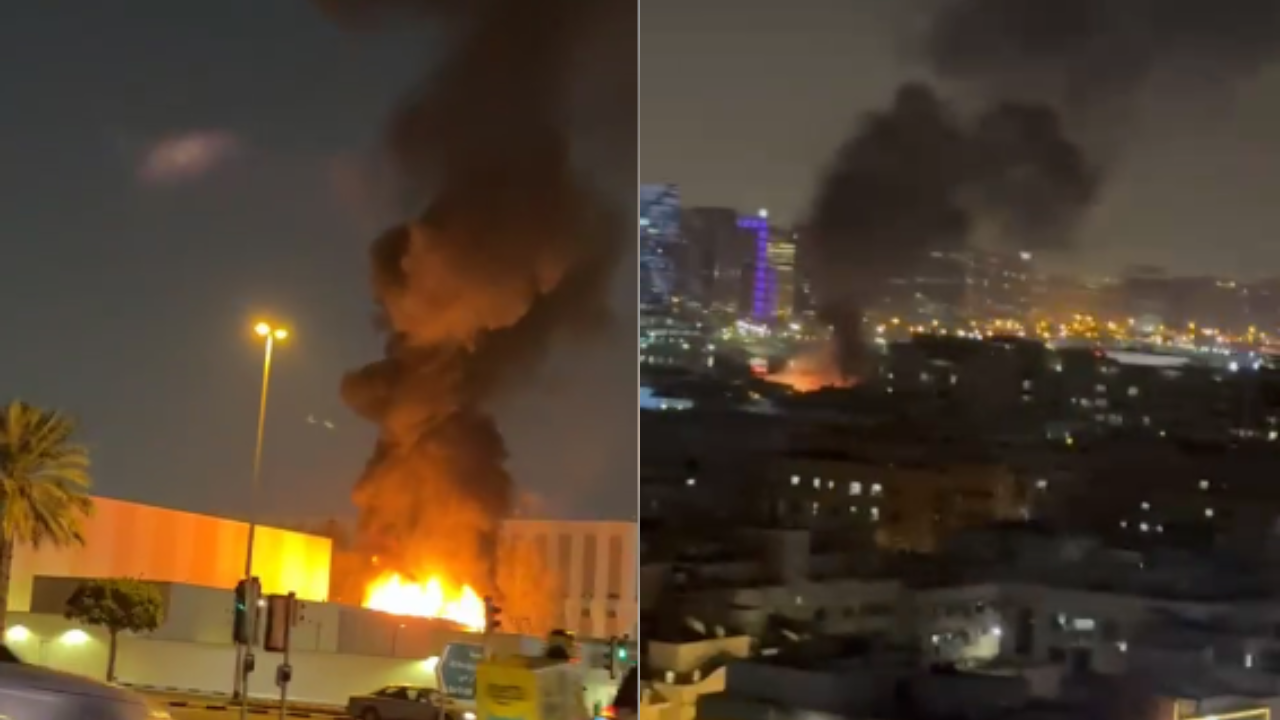
Dubai: Smoke was seen rising from an area near the United States Consulate in Dubai, according to witness accounts cited by Reuters.
There was no immediate official confirmation on the extent of damage or whether there were any casualties in the incident.
Earlier, the US embassy in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia’s capital, was also attacked. Authorities reported damage to the premises, but no casualties were recorded.
The developments come amid heightened tensions in the region, with Iran continuing to target US interests in the Middle East following deadly attacks launched on Saturday by Israel and the United States.
Near US embassy in Dubai pic.twitter.com/z5VTZNVxNO
— Sahil Shah (@thesahilsshah) March 3, 2026