Bengaluru (PTI): The Karnataka government has issued an advisory urging people to adhere to COVID-19 appropriate behaviour in view of newer sub-variants of Coronavirus being reported in neighbouring Maharashtra.
The health department has also advised people with symptoms such as cough, cold and fever to get tested at nearest hospitals and isolate themselves till the results are out. "In view of reporting newer sub-variants of Omicron BQ.1 (US variant) BA.2.3.20 apart from XBB, which is a recombinant of BA.2.75 and BJ.1 in Maharashtra and in the context of the ensuing festival season of Deepavali and Kannada Rajyothsava the following advisory is issued to General public, the Commissionerate of Health and Family Welfare said. "Those with fever, cough, cold, sore throat, breathing difficulty should compulsorily get tested immediately at the nearest hospital or health centres (preferably Rapid Antigen Test, if negative then RT-PCR, and get self-isolated till the results are received," the department said.
Those with breathing difficulties should seek urgent medical care, preferably in a hospital.
Face masking while indoors, in places with air-conditioning, not well-ventilated areas, closed places, in crowds and in health facilities (N-95 / medical masks). It is very important that elderly and Co-morbid wear face masks in public areas, the advisory read.
The department has asked people to observe festivities outdoors and avoid crowding indoors as far as possible.
Further, those who are due for booster or precautionary dose of vaccination would need to get vaccinated. It is important that those who are aged 60 years and above, and with co-morbidities (particularly not naturally infected previously) should get vaccinated early. Those who are immune-deficient and immunosuppressed, on renal dialysis, taking anticancer drugs, etc. are advised to get vaccinated on priority basis in consultation with their treating doctor, the advisory said.
The department said that the COVID Appropriate Behaviour (CAB) like coughing and sneezing into folded elbows, use of tissues, hand kerchief, not to blow nose and spit in public areas, hand washing with soap and water, avoiding close contact with symptomatic persons should be followed.
In addition to the general advisory, the department has also asked people to use environment friendly "green crackers" in the larger interest of public health and safety.
The department has also asked the authorities concerned in the districts and municipal areas to ensure the compliance of the same.
In view of reporting newer sub-variants of Omicron BQ.1 (US variant)
— K'taka Health Dept (@DHFWKA) October 25, 2022
BA.2.3.20 apart from XBB, which is a recombinant of BA.2.75 and BJ.1 in Maharashtra and in the context of the ensuing festival season of Deepavali & Kannada Rajyothsava the following advisory pic.twitter.com/VmBeYYoODL
Let the Truth be known. If you read VB and like VB, please be a VB Supporter and Help us deliver the Truth to one and all.
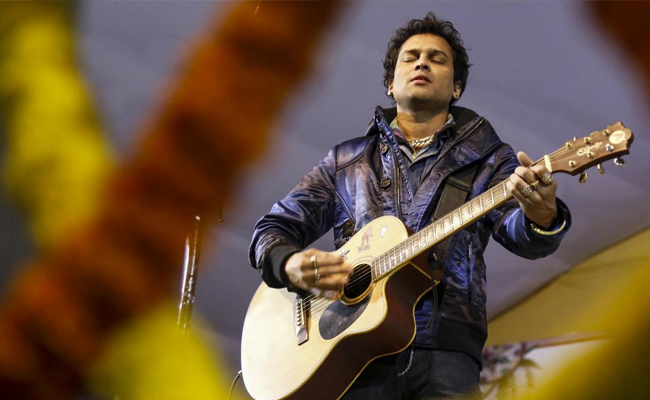
Singapore (PTI): Investigations into the death of singer Zubeen Garg are ongoing but so far no foul play is suspected, Singapore police have said.
Garg died under mysterious circumstances while swimming in the sea in Singapore on September 19.
The case is currently still being investigated by the Singapore Police Force (SPF), in accordance with the Singapore Coroners Act 2010, the police said on Thursday.
“Based on our investigations so far, the SPF does not suspect foul play in the death of Garg,” said the statement.
ALSO READ: 12 cases filed for pro-Pakistan slogans in 3 years, says Parameshwara
Upon completion of the investigations, the findings will be submitted to the State Coroner in Singapore, who will hold a Coroner’s Inquiry (CI), currently scheduled for January and February 2026.
A CI is a fact-finding process led by the Coroner to establish the cause and circumstances of death. Its findings will be made public upon conclusion, said the SPF.
Singapore police are committed to conducting a thorough and professional investigation into the case, it said.
“We seek the patience and understanding of the parties involved. Meanwhile, we urge the public not to speculate and spread unverified information,” said SPF.
A Special Investigation Team probing Garg's death charged four accused, including the singer’s secretary Siddhartha Sharma and festival organiser Shyamkanu Mahanta, with murder in a chargesheet filed in a court in India last week.
Garg was due to perform at the 4th Northeast India Festival at Suntec Singapore Convention and Exhibition Centre on September 20.